Introduction – Importance of Data in Datasets
“Information is the new oil.” Today information is wherever in each field. Whether you are an information researcher, advertiser, money manager, information expert, specialist, or you are in some other calling, you really want to play or try different things with crude or organized information. This information is so significant for us that it becomes essential to deal with and store it appropriately, with practically no mistake. While chipping away at these information, it means quite a bit to know the kinds of information to handle them and come by the right outcomes. There are two kinds of information: Subjective and Quantitative information, which are additionally ordered into:
The data in Datasets is classified into four categories:
- Nominal data.
- Ordinal data.
- Discrete data.
- Continuous data.
So there are 4 Types of Data in Datasets : Nominal, Ordinal, Discrete, and Continuous.
Presently business runs on information, and most organizations use information for their experiences to make and send off crusades, plan methodologies, send off items and administrations or evaluate various things. As indicated by a report, today, no less than 2.5 quintillion bytes of information are delivered each day.
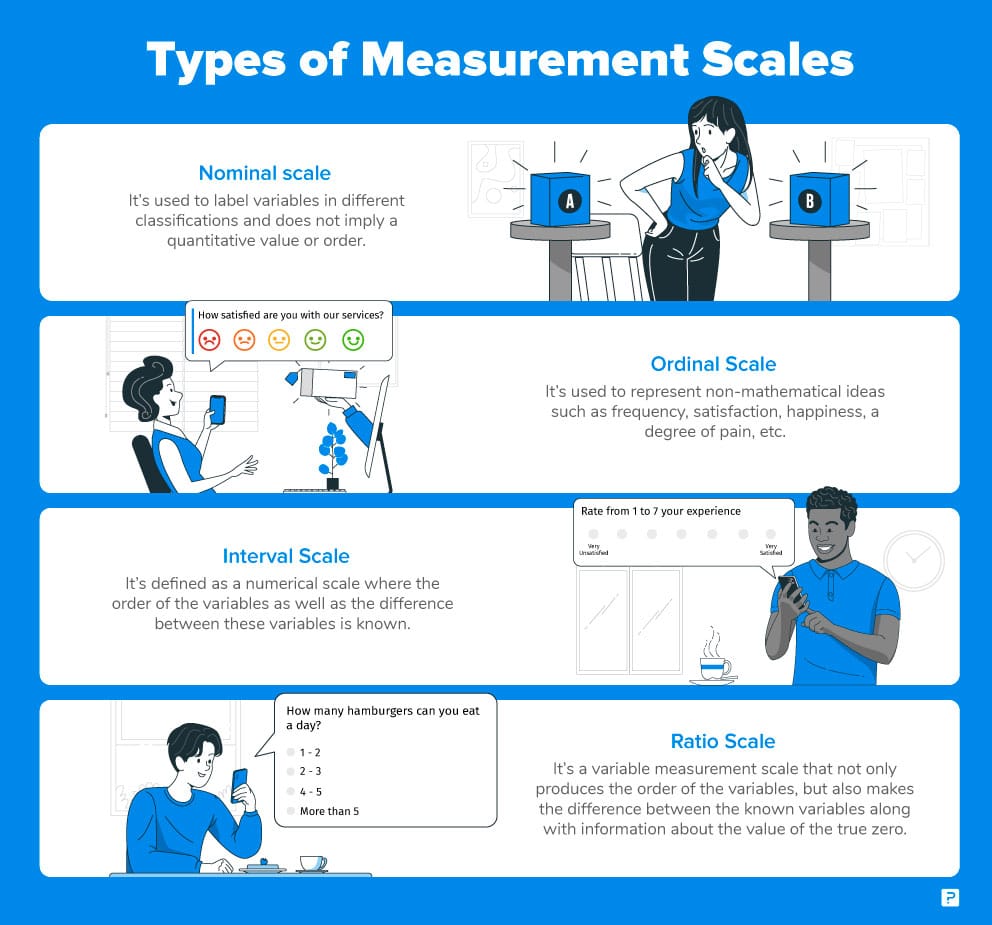
Subjective or Clear cut Information
Subjective or Clear cut Information is information that can’t be estimated or included in that frame of mind of numbers. These kinds of information are arranged by classification, not by number. That is the reason it is otherwise called Downright Information. These information comprise of sound, pictures, images, or text. The orientation of an individual, i.e., male, female, or others, is subjective information.
Subjective information tells about the view of individuals. This information assists economic analysts with understanding the clients’ preferences and afterward plan their thoughts and procedures in like manner.
Different instances of subjective information are :
- What language do you talk
- Most loved vacation spot
- Assessment on something (concur, deviate, or nonpartisan)
- Colors
The Subjective information are additionally grouped into two sections :
Ostensible Information
Ostensible Information is utilized to mark factors with no structure or quantitative worth. The shade of hair can be viewed as ostensible information, as one tone couldn’t measure up to another variety.
The name “ostensible” comes from the Latin name “nomen,” and that signifies “name.” With the assistance of ostensible information, we can’t do any mathematical errands or can’t provide any request to sort the information. These information have no significant request; their qualities are appropriated into unmistakable classifications.
Instances of Ostensible Information :
- Shade of hair (Blonde, red, Brown, Dark, and so on.)
- Conjugal status (Single, Bereft, Wedded)
- Ethnicity (Indian, German, American)
- Orientation (Male, Female, Others)
- Eye Tone (Dark, Brown, and so on.)
- Ordinal Information
Ordinal information have regular requesting where a number is available in a request by their situation on the size of some sort or another. These information are utilized for perception like consumer loyalty, satisfaction, and so on, however we can’t do any arithmetical assignments on them.
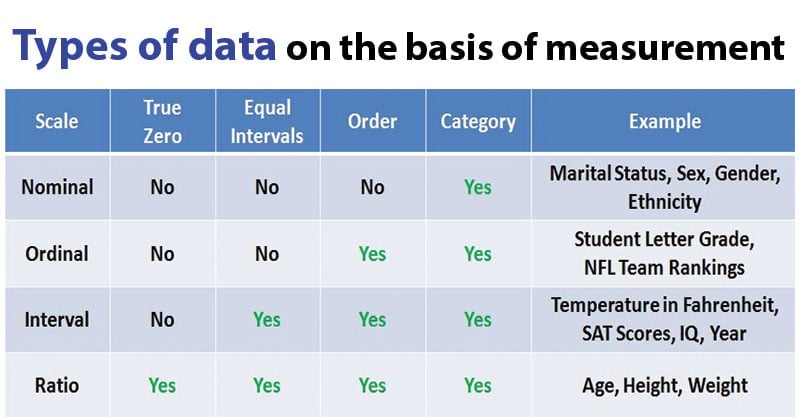
Ordinal information is subjective information for which their qualities have a general place of some sort or another. These sorts of information can be thought “in the middle among” subjective and quantitative information. The ordinal information just shows the groupings and can’t use for measurable examination. Contrasted with ostensible information, ordinal information have some sort of request that is absent in ostensible information.
Instances of Ordinal Information :
- At the point when organizations request criticism, experience, or fulfillment on a size of 1 to 10
- Letter grades in the test (A, B, C, D, and so forth.)
- Positioning of individuals in a contest (First, Second, Third, and so on.)
- Monetary Status (High, Medium, and Low)
- Training Level (Higher, Optional, Essential)
Difference between Nominal and Ordinal Data
| Nominal Data | Ordinal Data |
| Nominal data can’t be quantified, neither they have any intrinsic ordering | Ordinal data gives some kind of sequential order by their position on the scale |
| Nominal data is qualitative or categorical | Ordinal data is said to be “in-between” qualitative and quantitative |
| They don’t provide any quantitative value, neither can we perform any arithmetical operation | They provide sequence and can assign numbers to ordinal data but cannot perform the arithmetical operation |
| Nominal data cannot be used to compare with one another | Ordinal data can help to compare one item with another by ranking or ordering |
| Examples: Eye color, housing style, gender, hair color, religion, marital status, ethnicity, etc | Examples: Economic status, customer satisfaction, education level, letter grades, etc |
Quantitative Information
Quantitative information can be communicated in mathematical qualities, making it countable and including measurable information examination. These sorts of information are otherwise called Mathematical information. It responds to the inquiries like “how much,” “the number of,” and “how frequently.” For instance, the cost of a telephone, the PC’s slam, the level or weight of an individual, and so on, falls under quantitative information.
Quantitative information can be utilized for measurable control. These information can be addressed on a wide assortment of diagrams and outlines, for example, structured presentations, histograms, disperse plots, boxplots, pie diagrams, line charts, and so on.
Instances of Quantitative Information :
- Level or weight of an individual or item
- Room Temperature
- Scores and Stamps (Ex: 59, 80, 60, and so forth.)
- Time
The Quantitative information are additionally characterized into two sections :
- Discrete Information
- The term discrete means unmistakable or isolated. The discrete information contain the qualities that fall under numbers or entire numbers. The complete number of understudies in a class is an illustration of discrete information. These information can’t be broken into decimal or division values.
- The discrete information are countable and have limited esteems; their region is unimaginable. These information are addressed primarily by a reference chart, number line, or recurrence table.
Difference between Discrete and Continuous Data
| Discrete | Continuous |
|---|---|
| Discrete data are countable and finite; they are whole numbers or integers | Continuous data are measurable; they are in the form of fractions or decimal |
| Discrete data are represented mainly by bar graphs | Continuous data are represented in the form of a histogram |
| The values cannot be divided into subdivisions into smaller pieces | The values can be divided into subdivisions into smaller pieces |
| Discrete data have spaces between the values | Continuous data are in the form of a continuous sequence |
| Examples: Total students in a class, number of days in a week, size of a shoe, etc | Example: Temperature of room, the weight of a person, length of an object, etc |
Conclusion
In this article, we have examined the information types and their disparities. Chipping away at information is vital on the grounds that we want to sort out what sort of information it is and how to utilize it to receive important result in return. It is likewise essential to understand what sort of plot is appropriate for which information classification; it helps in information examination and perception. Working with information requires great information science abilities and a profound comprehension of various sorts of information and how to function with them.
Various kinds of information are utilized in research, examination, measurable investigation, information perception, and information science. This information assists an organization with breaking down its business, plan its methodologies, and assist with building an effective information driven dynamic cycle.
On the off chance that these information driven points got you keen on chasing after proficient courses or a lifelong in the field of Information Science. Sign on to our site and investigate courses conveyed by industry specialists.