Show
The field test has now Ethnicity transformed into a standard method for focusing on racial and ethnic partition in the work market. In an ordinary work market attempt (in any case called an audit or correspondence study), experts randomly consign an indication of race or personality to nonexistent CVs, follow positions and record contacts from supervisors.
Anyway long the sign assignment is sporadic, the qualifications in the contact rates across the social affairs can be treated as confirmation of detachment. Such investigations have now been driven in various countries [for progressing composing reviews, see Rich (2014); Zschirnt and Ruedin (2016); Bertrand and Duflo (2017); Baert (2018); and Neumark (2018)].
There is overwhelming confirmation that on ordinary organizations contact applicants from larger part bundles more consistently than up-and-comers from minority get-togethers. Racial and ethnic isolation in the work market is generally announced.

In this article, we present the outcomes of the essential ethnic isolation test coordinated in Russia. We base on two basic requests.
First and foremost, viewpoints of ethnic bigger parts towards different minority packs are not the same, and change as demonstrated by a comprehended hierarchy of leadership. In Western countries, minority social affairs of European start are ordinarily more commonly recognized than get-togethers of African and Asian start (Hagendoorn, 1995). Most field tests to date looked at one or a few minority get-togethers.
Without a doubt, even the greater audit focuses on sometimes had adequate verifiable capacity to give strong evaluations of the qualifications in contact rates across minority get-togethers. In this audit, we do an arrangement with 10 ethnic social occasions and a model size of in excess of 9,000 work frames that grants us to give reliable examinations of division to each get-together and explore the ethnic hierarchy for a long while in Russia.
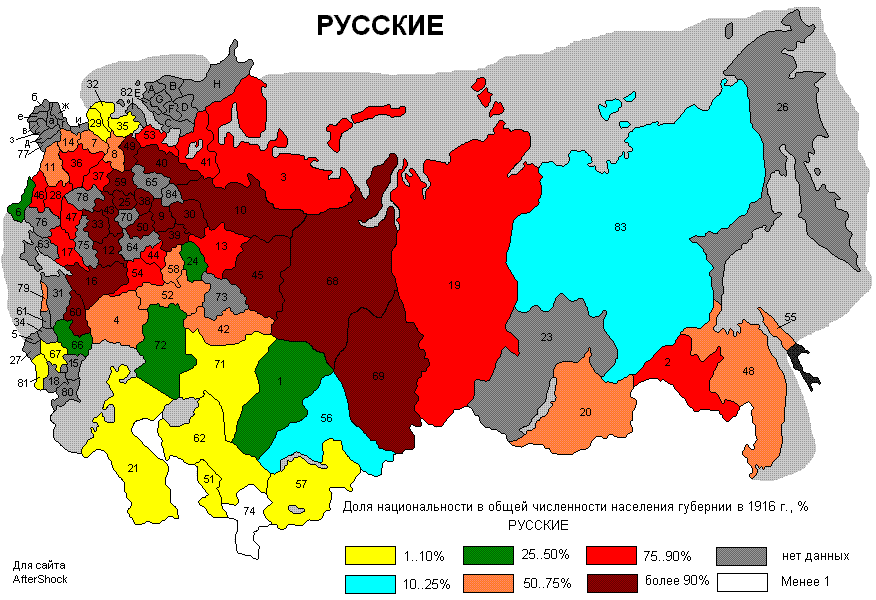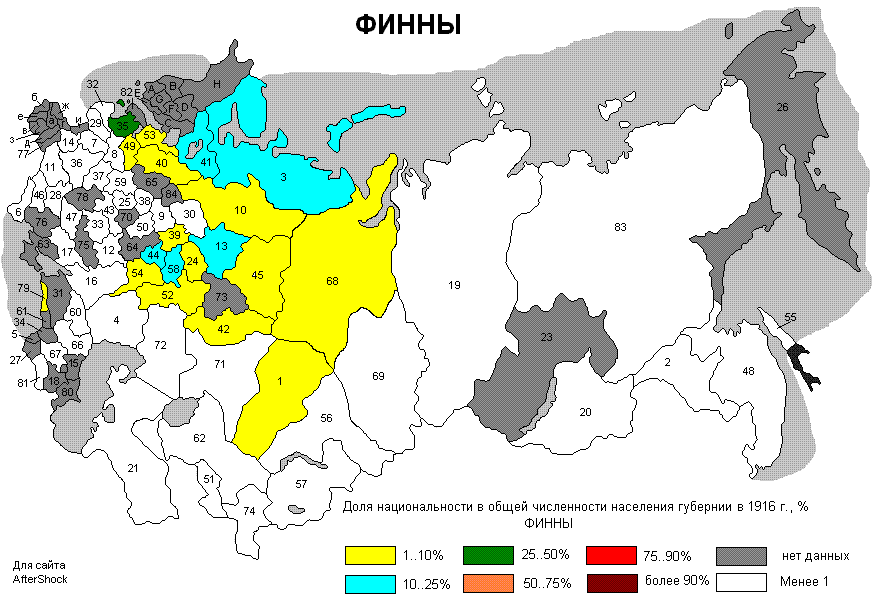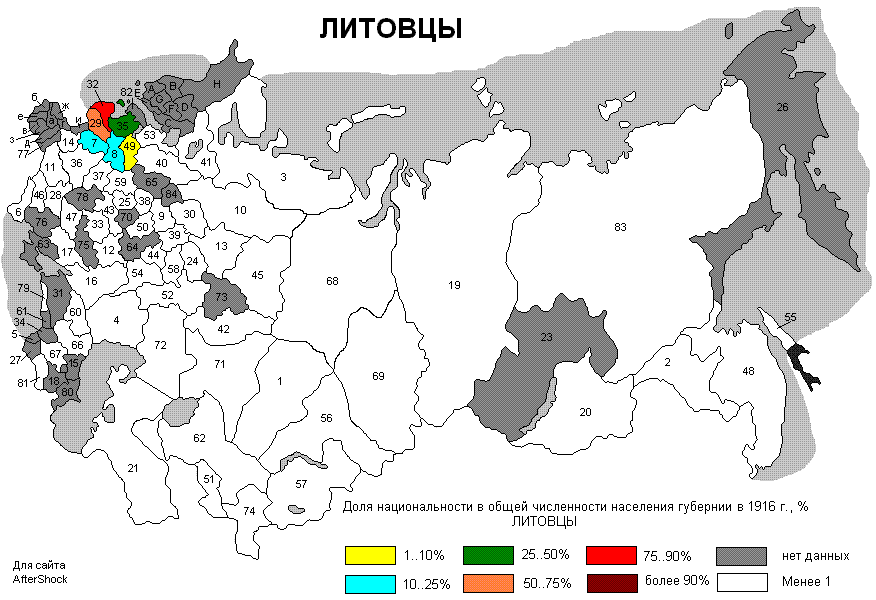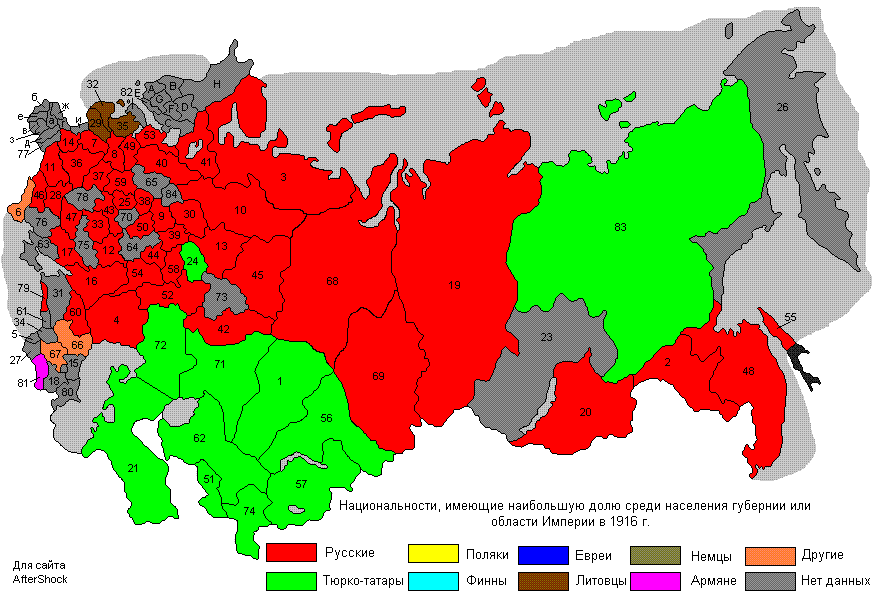
Second, we revolve around topographical assortment in isolation. Russia is a multi-ethnic association where, in specific areas, local ethnic get-togethers have an extraordinary institutional status. Are the instances of ethnic isolation and moderate framework the same or particular in ethnically heterogeneous, differentiated and ethnically Russian, regions?
To address this request, we coordinated our examination in four Russian metropolitan regions. Two of them (Moscow and St. Petersburg) are metropolitan locales, with by and large ethnically Russian masses. The other two metropolitan networks (Kazan and Ufa) are capitals of ethnic autonomies, with mixed ethnic Russian and local Muslim masses.
The results show great differentiations in the instances of ethnic isolation across these spaces. In Moscow and St. Petersburg, directors deceive recognizable ethnic minorities of Southern start anyway not against get-togethers of European start.
Abuse ethnic minority men is more grounded than that against ethnic minority women. Of course, in Kazan and Ufa, all ethnic get-togethers are treated by supervisors in around the same way, with the contact rates for most social events of Southern start being simply unimportantly, and not truly basically, lower than for get-togethers of European start.
Introduction (50 words): In this article, we delve into the results of a significant study conducted in Russia that focuses on assessing ethnic isolation. With a particular emphasis on two key research questions, we explore the findings and implications of the study, shedding light on the state of ethnic isolation within the country.
- Research Question 1: Extent of Ethnic Isolation (150 words): The first research question addressed in the study aimed to determine the extent of ethnic isolation within Russia. The findings revealed that ethnic isolation varies across regions and is influenced by factors such as geographical location, historical context, and ethnic diversity. In some areas, communities demonstrated a high degree of integration and interethnic interaction, fostering social cohesion. However, in certain regions, ethnic isolation was more prevalent, characterized by limited cross-cultural communication and minimal interethnic relationships.
- Research Question 2: Factors Contributing to Ethnic Isolation (150 words): The second research question focused on identifying the factors that contribute to ethnic isolation in Russia. The study uncovered several key drivers, including economic disparities, cultural differences, language barriers, and historical tensions. Socio-economic factors, such as unequal access to resources and opportunities, played a significant role in perpetuating ethnic isolation. Additionally, cultural preservation and a desire to maintain distinct ethnic identities influenced social interactions and limited intergroup communication.
- Implications and Recommendations (150 words): The study’s findings have important implications for addressing ethnic isolation in Russia. To promote greater social integration and cohesion, policymakers should prioritize efforts to reduce economic disparities, provide equal access to resources and opportunities, and foster cross-cultural understanding. Encouraging initiatives that facilitate interethnic dialogue, cultural exchange, and community-building activities can help bridge divides and promote a sense of belonging among diverse ethnic groups. Additionally, investing in education and language programs that promote multilingualism and intercultural competence can facilitate better communication and understanding between communities.
It is crucial to engage local communities, ethnic organizations, and civil society in the development and implementation of strategies aimed at reducing ethnic isolation. Collaboration and cooperation among stakeholders can foster a sense of ownership and ensure that interventions are tailored to the specific needs and contexts of different regions within Russia.
Conclusion (50 words): The study conducted in Russia sheds light on the extent of ethnic isolation and the factors contributing to this phenomenon. By understanding the challenges and identifying potential strategies for addressing ethnic isolation, policymakers and communities can work together to foster greater social integration, promote cultural diversity, and build inclusive societies Ethnicity
Henceforth, the responsibilities of this article to the composition on ethnic isolation are the going with.
We show that (I) ethnic isolation in Russia is for the most part planned against social affairs of Southern start, with very little persecution get-togethers of European start (ethnic moderate framework); (ii) men from ethnic minorities face more grounded partition differentiated and women; and (iii) the model and level of ethnic isolation change across regions with moving ethnic course of action of the general populations and the chronicled background of ethnic between pack relations.
These revelations add to the composition on the between pack distance and contact theory showing how the chronicled background of between bundle contact and institutional approaches can lighten the sensation of ethnic social event risk.
Introduction (50 words): Ethnic isolation is a pressing issue that hinders social cohesion and inclusivity. This article aims to explore the responsibilities of addressing ethnic isolation and promoting social integration. By understanding the challenges, recognizing the benefits of diversity, and implementing inclusive practices, we can foster a more inclusive and harmonious society Ethnicity
- Understanding Ethnic Isolation (100 words): Ethnic isolation refers to the separation or exclusion of individuals or communities based on their ethnic or cultural background. It can manifest in various forms, including residential segregation, limited social interactions, and lack of representation. Ethnic isolation can perpetuate stereotypes, increase social inequalities, and impede the formation of diverse and inclusive communities Ethnicity
- Challenging Assumptions and Stereotypes (150 words): Addressing ethnic isolation requires challenging assumptions and stereotypes that contribute to social divisions. Education and awareness campaigns can help debunk stereotypes and promote understanding and empathy among diverse groups. Encouraging individuals to engage in open dialogues, share experiences, and celebrate cultural diversity can bridge gaps and break down barriers Ethnicity
- Building Inclusive Communities (150 words): Creating inclusive communities is essential for combating ethnic isolation. Local governments, community organizations, and institutions can play a pivotal role in fostering social integration. Initiatives such as community events, cultural exchanges, and language programs promote interaction and create opportunities for individuals from different backgrounds to connect and build meaningful relationships. Affordable housing policies that encourage mixed communities and ensure diverse representation in decision-making processes are also crucial Ethnicity
- Enhancing Access to Services and Opportunities (100 words): Ethnic isolation often stems from limited access to services and opportunities. Efforts should be made to ensure equitable access to quality education, healthcare, employment, and social support systems. Tailored programs and resources that address language barriers, cultural sensitivity, and inclusivity can empower individuals and communities, facilitating their integration into society.
- Promoting Social Integration in Policy and Practice (100 words): Addressing ethnic isolation requires a comprehensive approach that integrates policies and practices promoting social integration. Governments should enact inclusive legislation and policies that protect minority rights, foster diversity, and combat discrimination. Integration should be considered in urban planning, with diverse neighborhoods and public spaces designed to encourage interaction and engagement Ethnicity
Conclusion (50 words): Addressing ethnic isolation is a shared responsibility that requires collective efforts to promote social integration. By challenging assumptions, building inclusive communities, enhancing access to services and opportunities, and integrating social integration in policies and practices, we can create a society that values diversity and thrives on inclusivity. Together, we can break down the barriers of ethnic isolation and foster a more cohesive and united society Ethnicity

Ethnicity Hierarchies, Discrimination, and Local Context
Human social orders will overall be facilitated as get-together based levels of leadership (Sidanius and Pratto, 2001). Various progressed social orders are multi-racial and multi-ethnic and join huge ethnic minorities, often both local and of traveler starting. Researchers of between pack social distance battle that cultural position contrasts across racial and ethnic get-togethers Ethnicity
In various Western social orders North Europeans have the most vital status, followed by South and Eastern Europeans, Asians, and Africans (Hagendoorn, 1995).
This ethnic levels of leadership can be consistent across time (Kleg and Yamamoto, 1998; Ford, 2011) and is oftentimes recognized both by the ethnic larger part and by minorities (Verkuyten, Hagendoorn and Masson, 1996; Zick et al., 2001), though some ethnic cutoff points can darken after some time (Alba, 2005). Survey evidence avows that points of view of local people towards pariahs of different ethnic start can change unequivocally. Ethnic speculations are pack unequivocal.
In the United States, respondents rate White Americans higher than Asians, and Asians higher than African Americans and Hispanics, on most traits (Bobo and Massagli, 2001). The British public recognizes transients from Australia, but many are more far fetched with respect to Europeans, and especially untouchables from Africa, the Caribbean area and South Asia (Ford, 2011).
Correspondence studies have commonly been unraveled as tries to evaluate partition in the work market. As most assessments, they often need outside authenticity and generalizability (Baldassarri and Abascal, 2017). By plan, these assessments are limited to several occupations, capacities, regions, racial and ethnic social events, and channels of enlistment Ethnicity
When in doubt, we can simply accumulate data about requesting to interviews rather than veritable work and pay offers. Extrapolating exploratory appraisals of isolation in enrollment to various spaces of the work market anticipates that we should make various assumptions Ethnicity
Theoretically, correspondence thinks generally added to disengaging genuine from taste-based isolation and have been isolated from the composing examining the get-together risk and contact speculations that routinely support the sociological examinations of the mindsets towards laborers. Regardless, correspondence tests can in like manner be seen as an instrument for assessing bundle express ethnic predisposition, as uncovered in supervisors’ enlisting decisions.
While not coming from comprehensively specialist tests, exploratory examinations of ethnic predisposition partake in the critical advantage of restricting social appeal tendency. The point of convergence of investigation then, shifts, from giving reasonable evaluations of work market isolation, to dissecting the overall standings of racial and ethnic social affairs Ethnicity
Most correspondence focuses on intricate two or three ethnic minority social events and were not planned to evaluate bundle assortment in detachment. Exactly when various social events were involved the results oftentimes showed that in Western countries minorities of European start were managed exceptionally differentiated and minorities of non-European start (Baldini and Federici, 2011; Booth, Leigh and Varganova, 2012; Carlsson and Eriksson, 2015; Acolin, Bostic and Painter, 2016; Baert et al., 2017; Lancee, 2019; Vernby and Dancygier, 2019).
These revelations confirm the presence of an ethnic hierarchy of leadership in the work market and are consistent with the social distance investigation, and outline confirmation of ethnic differentiations in business and wages (Heath and Cheung, 2007). Not all minorities are something almost identical, and some are managed better contrasted with others Ethnicity
Blumer (1958) comprehensively suggested that racial predisposition emerges when people from the predominant social occasion see a test, to their common financial prosperity, from subordinate out-get-togethers. The get-together peril hypothesis became one of the backbones of the composition on mindsets towards outsiders (Ceobanu and Escandell, 2010).

Precisely, it is consistently attempted by looking at the relationship among predisposition and veritable or saw transient social event size, possibly interceded by financial conditions (Quillian, 1995; Semyonov, Raijman and Gorodzeisky, 2006). Larger part people may feel more sabotaged in places with a further degree of ethnic minority people, especially when the economy is poor. The assistance, from observational survey confirmation, of the social affair peril theory has been mixed Ethnicity
Exactly when the examination is driven at the neighborhood rather than the country level, a couple of assessments confirm the connection between minority pack size and against specialist inclination in Europe (Markaki and Longhi, 2013), however others disregard to find this association (Hjerm, 2009; Rustenbach, 2010).
One more grounded theoretical approach that is consistently inspected in this composing is the contact hypothesis (Allport, 1954). Under explicit conditions, experiencing positive contact with people from out-social affairs may reduce inclination (Pettigrew and Tropp, 2006). While the social affair risk and contact theories may make conflicting figures, both of them stress the meaning of consistent parts for between bundle relations Ethnicity
The two theories deduce that the level of isolation would change across regions with different racial and ethnic people associations. Every one of the more ethnically various spots may invigorate between bundle contact that will lessen predisposition. Of course, the surge of ethnically different masses may trigger the sensation of social affair risk and prompt negative attitudes towards newbies. Correspondence studies showed that in specific spots (France, London) dwelling exploitation minorities was more grounded in regions with more outsiders (Carlsson and Eriksson, 2014.
Introduction (50 words): Ethnicity hierarchies and discrimination persist as significant challenges in societies worldwide, often rooted in historical, cultural, and socio-economic factors. This article aims to explore the interplay between ethnicity hierarchies, discrimination, and the local context. By understanding the complexities of these dynamics, we can work towards creating more equitable and inclusive communities Ethnicity
- Ethnicity Hierarchies: Origins and Impact (150 words): Ethnicity hierarchies refer to the social structures and perceptions that assign different values or status to ethnic or racial groups. These hierarchies are often shaped by historical legacies, power dynamics, and cultural prejudices. They can lead to unequal access to resources, opportunities, and social mobility. Recognizing and challenging these hierarchies is crucial for promoting social justice and fostering inclusive communities Ethnicity
- Discrimination and its Forms (150 words): Discrimination based on ethnicity is a pervasive issue that manifests in various forms, including systemic discrimination, institutional biases, interpersonal prejudice, and microaggressions. It can result in exclusion, marginalization, and unequal treatment. Discrimination affects individuals’ well-being, access to education, employment opportunities, and social interactions. Combating discrimination requires addressing both overt and subtle biases, promoting awareness, and implementing policies that ensure equal rights and opportunities for all Ethnicity
- Local Context and Intersectionality (150 words): The local context plays a significant role in shaping ethnicity hierarchies and discrimination. Historical events, cultural norms, and economic factors influence how ethnic groups are perceived and treated within specific communities. It is crucial to recognize the intersectionality of identities, considering the overlapping effects of race, ethnicity, gender, class, and other social categories. By understanding the local context, including community dynamics, power structures, and historical narratives, we can better address and dismantle ethnicity hierarchies and discrimination Ethnicity
- Promoting Inclusion and Equity (100 words): Addressing ethnicity hierarchies and discrimination requires collective action and systemic change. Education and awareness campaigns can challenge stereotypes and biases, fostering understanding and empathy. Advocacy for inclusive policies and practices, such as anti-discrimination legislation, affirmative action, and diverse representation, is essential. Encouraging dialogue, fostering intercultural exchange, and promoting equal opportunities are vital steps towards creating more inclusive and equitable communities Ethnicity
Conclusion (50 words): Ethnicity hierarchies and discrimination are complex issues that require a multifaceted approach. By understanding the origins and impact of ethnicity hierarchies, recognizing and addressing discrimination in its various forms, and considering the local context, we can strive towards fostering inclusive societies that celebrate diversity, promote equity, and combat prejudice and discrimination Ethnicity