What are translators?
translators:
- Translators is any program written in a significant level language is known as source code. In any case, PCs can’t comprehend source code. Before it tends to be run, source code should initially be converted into a structure which a PC comprehends.
- is a program that converts source code into machine code.
By and large, there are three kinds of translators:
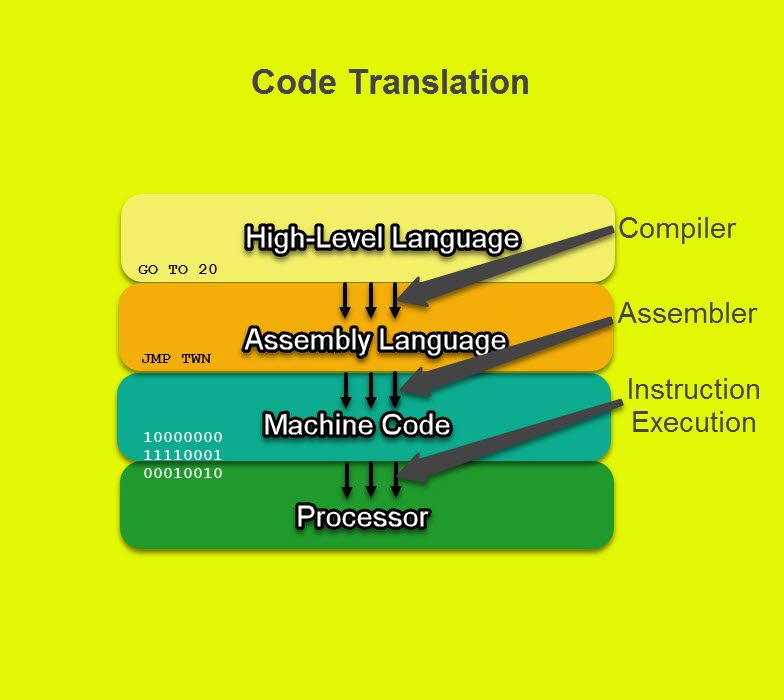
Compilers:
A compiler takes the source code in general and makes an interpretation of it into machine code across the board go. When changed over, the item code can be run unassisted whenever. This interaction is called
gathering.
Compilers enjoy a few benefits:
- Assembled programs run rapidly, since they have previously been interpreted.
- A gathered program can be provided as an executable record.
- An executable record is a document that is prepared to run.
- Since an executable document won’t be quickly changed, developers like to supply executables as opposed to source code.
- Compilers improve code. Enhanced code can run speedier and take up less memory space.
Compilers additionally have burdens:
- The source code should be re-gathered each time the software engineer changes the program.
- Source code assembled on one stage won’t run on another – the machine code is intended for the processor’s engineering.
Interpreters:
A translator makes an interpretation of source code into machine code one guidance at a time. It is like a human interpreter deciphering what an individual says into another dialect, sentence by sentence, as they talk. The subsequent machine code is then executed right away. The cycle is called understanding.
Translators enjoy a few benefits:
- Directions are executed when they are deciphered.
- Blunders can be immediately spotted: when a mistake is found, the program quits running and the client is advised at what part of the program the understanding has fizzled. This makes mediators incredibly helpful while creating programs.
Mediators likewise have a few disservices:
- Deciphered programs run gradually as the processor needs to trust that every guidance will be interpreted before it tends to be executed.
- Furthermore, the program must be deciphered each time it is run.
- Mediators don’t deliver an executable document that can be appropriated. Subsequently, the source code program must be provided, and this could be altered without authorization.
- Mediators don’t enhance code – the deciphered code is executed for what it’s worth.
Assemblers:
Constructing agents are a third kind of interpreter. The reason for a constructing agent is to decipher low level computing construct into machine code.
While compilers and translators produce many machine code guidelines for every significant level guidance, constructing agents make one machine code guidance for every gathering guidance.
What is translation?
Translation:
Is the action that comprises of grasping the significance of a text in one language, called “source text” or “result text”, to deliver a text with comparable importance in another dialect, called deciphered text or “target text”.
In other words, translation is the most common way to adapt a message from one language to another to keep up with the first message and correspondence.
In the cutting edge world, there are three kinds of translation :
Human translation:
Is the most common way of deciphering text starting with one language then onto the next performed by a human interpreter. This strategy delivers the most reliable and dependable of a wide range of translation, bringing about regular sounding, valid substance.
Machine translation:
Is a PC helped interpretation process in which a machine endeavors to decipher text starting with one language then onto the next. It is frequently utilized for huge scope projects thanks for its cost potential benefit. A mechanized cycle is likewise quicker than human and different sorts of translation.
Post-altered translation:
Post-altered translation- otherwise called Post-editing Machine Translation (PEMT) – is a type of PC interpretation joined with a human component. Human etymologists adjust machine-made an interpretation of text to work on the quality. The outcomes are made more exact, steady, and legitimate.
These sorts of interpretation find some kind of harmony among human and machine interpretations. Post-altered interpretation is in this way an answer when human interpretation isn’t a choice because of cost or time requirements, however when precision is of high significance.
These three instances of translation are suitable approaches to delivering content into another dialect.