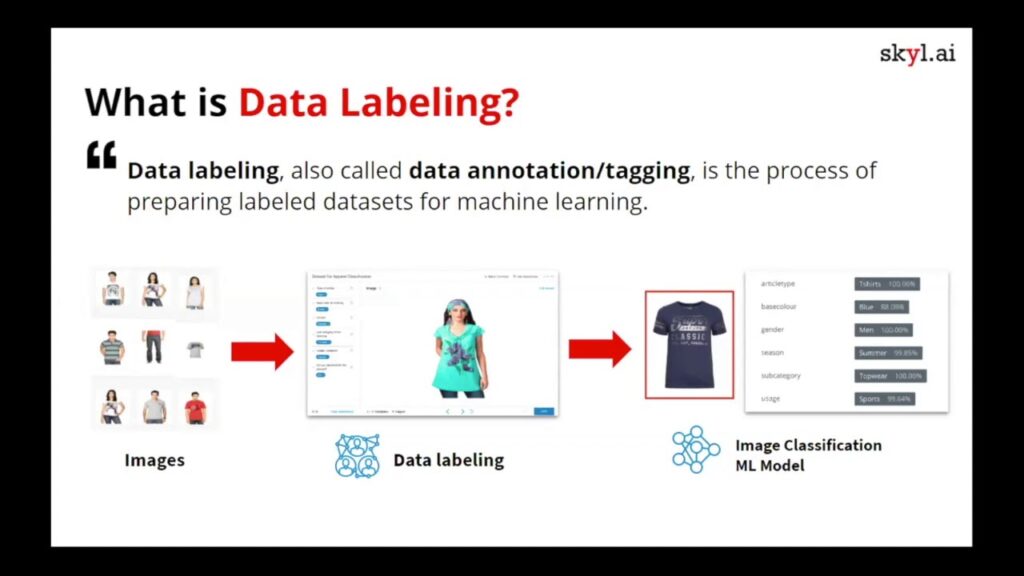
3D label point cloud data annotation includes: feature extraction, 3D reconstruction and matching, and point cloud model extraction.
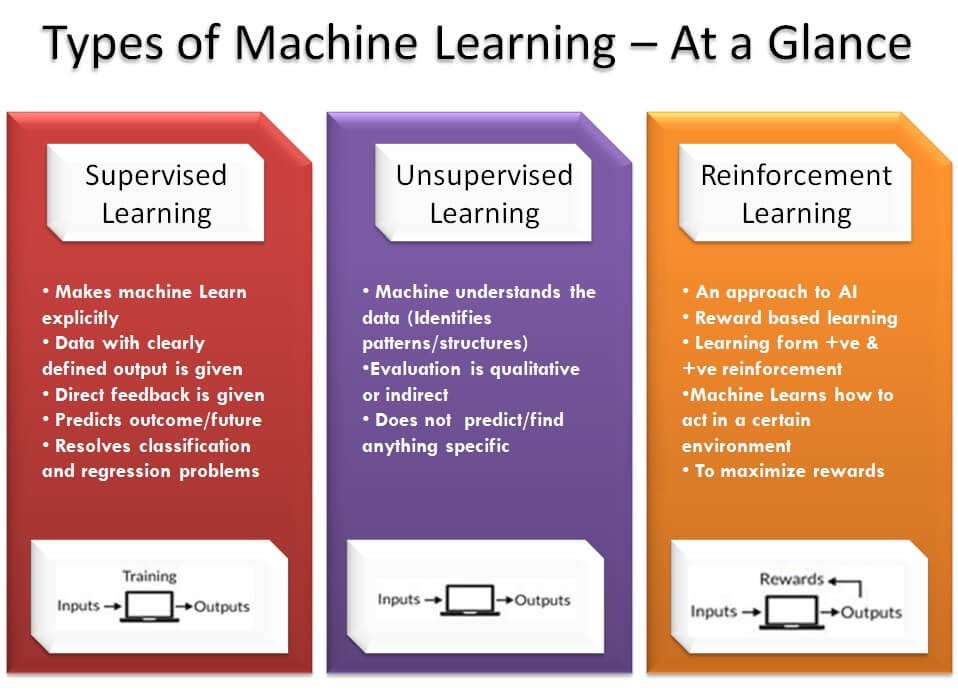
Feature extraction: It refers to measuring the target surface or internal point cloud, obtaining the target surface or internal data, and comparing it with the original point cloud to determine whether there is similarity between the points.
Three-dimensional reconstruction: refers to the three-dimensional reconstruction of the surface or internal structure of an object in three-dimensional space.
Point cloud model extraction: refers to the extraction of object entities and their characteristics through the data information of point clouds, and the establishment of corresponding point databases.
These tasks seem simple, but in fact they involve a lot of knowledge in different fields. Here I will only introduce the most basic and important parts. This article mainly introduces how to accurately extract the point coordinates in the lidar 3D point cloud, and at the same time explains in detail in combination with actual work. Finally, we also put forward some suggestions for these parts for reference.
1. Feature extraction
According to the obtained point cloud data, it is divided into several small areas, and each small area contains one or more known points and a group of unknown points.
(1) Point cloud feature extraction: Various methods are used for point cloud feature extraction, mainly including the following two methods: (2) Feature-based data matching: matching feature points of known planes.
2. 3D reconstruction and matching
The 3D reconstruction and matching work is mainly to analyze the data through the computer, and then determine the position in the 3D space, and combine the obtained information with the map matching to realize the automatic extraction of the 3D coordinates.
Before point cloud annotation, we first need to obtain the point cloud vector of the measured object, which is what we call the target point cloud. Then, we establish a set of feature point vectors (feature point pairs) in the target point cloud, which can be 3D entities or internal structures. Secondly, we match and calculate it with the existing 3D coordinate system through the point cloud vector to obtain an accurate 3D model.
The above two steps are the most basic work, and there is still a lot of tedious work waiting for us to do in the future: for example: calculate, reconstruct and match the 3D coordinates of each 3D entity; combine the obtained information with map matching, etc.
3. Point cloud model extraction
Through the data information of the point cloud, the object entity and its characteristics are extracted, and the corresponding point database is established. Point cloud data is a part of the 3D world, so the point cloud coordinates consistent with the 3D world can be obtained through feature extraction and model extraction.
3D point cloud data labeling status:
At present, there are many companies engaged in lidar data collection and labeling in China, but most of them are in the initial stage. They do not have a deep understanding of the basic algorithms of lidar, such as gross error elimination, multi-target detection, laser ranging and 3D reconstruction. However, there is no uniform specification for technologies such as 3D point cloud model recognition and point cloud data matching.
In addition, there is another situation: for some large-scale and complete types of 3D point cloud data annotations , in order to reduce costs and speed up project progress, some unstructured point clouds are often simply processed. Therefore, in order to really do a good job in the recognition and matching of 3D point cloud models, we need to have a deeper understanding of the basic principles and algorithms of 3D data annotation and feature extraction.
In practical applications, 3D feature extraction and model recognition often need to be performed simultaneously. Because there is a certain degree of angle difference between the target and other objects on the ground, it is necessary to collect multiple points on the same target and obtain the distance between the target and other objects on the ground through a series of different measurement methods. angular difference, thereby determining its distance.