Dhudhuroa Language is an integral part of culture and identity. It shapes the way people think, communicate, and understand the world around them. Indigenous languages hold a wealth of knowledge about the environment, traditional practices, and spiritual beliefs of their communities. They are repositories of cultural heritage, passed down through generations.
The loss of indigenous languages has a profound impact on indigenous communities. It erodes cultural diversity and weakens the connection between individuals and their ancestral roots. Language loss can lead to a loss of traditional knowledge, as many indigenous languages have specific vocabulary and concepts that are not easily translated into other languages. It also affects the sense of belonging and self-esteem of indigenous individuals, as language is closely tied to their identity.
The History and Significance of Dhudhuroa Language
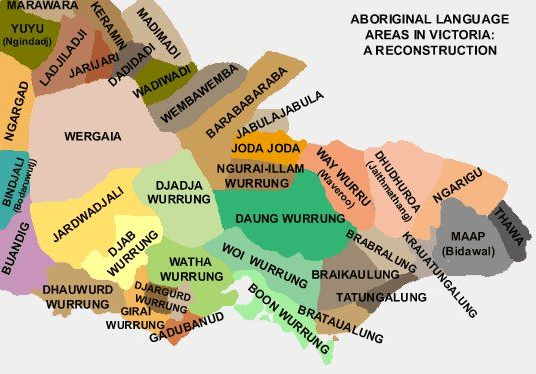
The Dhudhuroa people are an indigenous group from southeastern Australia, specifically from the region around the Snowy Mountains in New South Wales and Victoria. The Dhudhuroa language is part of the Yuin-Kuric language family, which includes several other indigenous languages spoken in the region.
The Dhudhuroa language has deep historical and cultural significance for the community. It is a key element in preserving their unique identity and heritage. The language contains rich oral traditions, stories, songs, and ceremonies that have been passed down through generations. It is also closely tied to the land and environment, with specific words and concepts related to local flora, fauna, and natural features.
Challenges Faced in the Preservation of Dhudhuroa Language
Like many indigenous languages around the world, Dhudhuroa is facing the threat of extinction. Several factors contribute to the decline of the language. Historical colonization, forced assimilation, and government policies that discouraged the use of indigenous languages have all played a role in language loss. The Dhudhuroa people were forcibly removed from their traditional lands and experienced significant disruption to their way of life.
Revitalizing an endangered language like Dhudhuroa poses numerous challenges. One major obstacle is the lack of fluent speakers. Many elders who were fluent in the language have passed away, and younger generations have not had the opportunity to learn it. Additionally, there is a lack of resources, such as dictionaries and teaching materials, which makes it difficult to teach and learn the language.
The Role of Linguistics in Revitalizing Dhudhuroa Language
| Challenges Faced in the Preservation of Dhudhuroa Language |
|---|
| Lack of speakers |
| Lack of written resources |
| Lack of funding for language preservation programs |
| Lack of interest from younger generations |
| Difficulty in finding qualified language teachers |
| Loss of traditional cultural practices and values |
| Impact of colonization and assimilation policies |
Linguistics plays a crucial role in revitalizing endangered languages like Dhudhuroa. Linguistic research helps document and analyze the structure, grammar, and vocabulary of the language. This information is essential for creating teaching materials, dictionaries, and language learning resources.
Linguists also work closely with indigenous communities to develop language revitalization programs. They collaborate with community members to create language learning materials that are culturally relevant and engaging. Linguistic research can also help identify patterns and similarities between related languages, which can aid in language revitalization efforts.
There have been successful examples of language revitalization efforts around the world. For instance, the Maori language in New Zealand has experienced a revival through community-led initiatives and government support. By incorporating Maori into education, media, and daily life, the language has been able to thrive and be passed on to future generations.
Community Efforts in Promoting the Use of Dhudhuroa Language
The Dhudhuroa community has been actively involved in revitalizing their language. Community-led initiatives have played a crucial role in promoting the use of Dhudhuroa and passing it on to younger generations. These efforts include language classes, cultural events, and the development of teaching materials.
Language classes are held regularly to teach Dhudhuroa to community members of all ages. These classes provide an opportunity for people to learn the language in a supportive and immersive environment. Cultural events, such as storytelling sessions and language immersion camps, are also organized to promote the use of Dhudhuroa and create a sense of pride and belonging among community members.
The development of teaching materials is another important aspect of community-led language revitalization efforts. The Dhudhuroa community has worked with linguists and educators to create resources such as dictionaries, grammar guides, and language learning apps. These materials are designed to be accessible and engaging, making it easier for people to learn and use the language.
The Impact of Language Loss on Indigenous Cultures

Language loss has a profound impact on indigenous cultures. Language is closely tied to cultural practices, rituals, and traditional knowledge. Many indigenous languages have specific vocabulary and concepts that are not easily translated into other languages. When a language is lost, this unique knowledge is also lost.
Language loss also affects the transmission of cultural values and beliefs. Indigenous languages often contain stories, myths, and legends that convey important moral lessons and cultural norms. Without the language to pass on these stories, future generations may lose touch with their cultural heritage.
Furthermore, language loss can lead to a loss of identity and self-esteem among indigenous individuals. Language is a fundamental part of one’s identity, shaping the way people think, communicate, and understand the world around them. When a language is lost, individuals may feel disconnected from their ancestral roots and struggle with their sense of belonging.
Strategies for Teaching Dhudhuroa Language to Future Generations
Teaching indigenous languages to future generations requires a multifaceted approach. Language teaching strategies should be tailored to the specific needs and context of the community. Some effective strategies include immersion programs, intergenerational learning, and the use of technology.
Immersion programs provide an immersive and intensive language learning experience. Participants are surrounded by the language and encouraged to use it in everyday situations. This approach helps develop fluency and a deeper understanding of the language and culture.
Intergenerational learning is another effective strategy for teaching indigenous languages. This involves bringing together elders, fluent speakers, and younger generations to create a supportive learning environment. Elders can share their knowledge and experiences, while younger generations can learn from their wisdom and guidance.
Technology can also play a significant role in language revitalization efforts. Language learning apps, online resources, and interactive multimedia materials can make language learning more accessible and engaging for younger generations. These tools can be used in conjunction with traditional teaching methods to create a blended learning experience.
Incorporating Dhudhuroa Language into Education and Daily Life
Incorporating the Dhudhuroa language into education and daily life is crucial for its preservation. Education plays a vital role in language revitalization efforts, as it provides a structured and systematic approach to language learning. By incorporating Dhudhuroa into the curriculum, students can learn the language from an early age and develop fluency over time.
Daily life is another important context for language use. Creating opportunities for people to use Dhudhuroa in their everyday interactions helps reinforce its importance and encourages its continued use. This can be done through community events, signage in the language, and media that promotes the use of Dhudhuroa.
Successful examples of language integration can be seen in places like Wales, where Welsh is taught in schools and used in government institutions. By incorporating the language into various aspects of daily life, Welsh has been able to thrive and be passed on to future generations.
The Connection Between Language and Identity
Language plays a crucial role in shaping identity. It is not just a means of communication, but also a reflection of one’s culture, heritage, and worldview. Language is closely tied to one’s sense of belonging and self-esteem.
For indigenous communities, language is an integral part of their identity. It connects them to their ancestral roots, their land, and their cultural practices. When a language is lost, it can have a profound impact on the identity of indigenous individuals, as they may feel disconnected from their heritage and struggle with their sense of belonging.
Preserving indigenous languages like Dhudhuroa is therefore essential for maintaining the cultural identity of indigenous communities. By preserving their languages, indigenous communities can pass on their unique knowledge, traditions, and values to future generations.
Celebrating the Richness of Indigenous Languages and Cultures
It is crucial to celebrate and value indigenous languages and cultures. Indigenous languages are not just a relic of the past; they are living languages that continue to evolve and adapt to modern times. They hold a wealth of knowledge, wisdom, and cultural heritage that enriches our collective human experience.
Language preservation efforts require collaboration and support from governments, educational institutions, linguists, and the wider community. Governments can provide funding and resources for language revitalization programs. Educational institutions can incorporate indigenous languages into their curriculum. Linguists can conduct research and develop teaching materials. And the wider community can show support by learning about indigenous languages, attending cultural events, and promoting their use.
In conclusion, the preservation of indigenous languages like Dhudhuroa is crucial for maintaining cultural diversity and ensuring the survival of unique knowledge and traditions. Efforts are being made to revitalize Dhudhuroa through community-led initiatives, linguistic research, and the incorporation of the language into education and daily life. By celebrating and valuing indigenous languages and cultures, we can contribute to the preservation of these rich and vibrant aspects of our shared human heritage.
If you’re interested in exploring the fascinating world of indigenous languages, you might also enjoy reading about the Dhudhuroa Language. Dhudhuroa is an endangered language spoken by the Dhudhuroa people of Australia. To learn more about this unique language and its cultural significance, check out this article: Discovering the Fascinating World of Aka Kede Language: A Journey into the Heart of an Endangered Tongue.
FAQs

What is Dhudhuroa Language?
Dhudhuroa Language is an indigenous Australian language spoken by the Dhudhuroa people of Victoria, Australia.
How many people speak ?
Currently, there are no known fluent speakers of Dhudhuroa Language. However, efforts are being made to revive the language.
What is the history ?
Dhudhuroa Language has a long history, with evidence of its use dating back thousands of years. However, due to colonization and the forced removal of indigenous people from their lands, the language has been in decline since the 19th century.
What efforts are being made to revive ?
Efforts to revive Dhudhuroa Language include language documentation, community language classes, and the creation of language resources such as dictionaries and grammar guides. The Dhudhuroa Language Program is also working to promote the language and its culture.
What is the significance of preserving ?
Preserving Dhudhuroa Language is important for the cultural identity and well-being of the Dhudhuroa people. It also contributes to the preservation of Australia’s linguistic diversity and cultural heritage.
