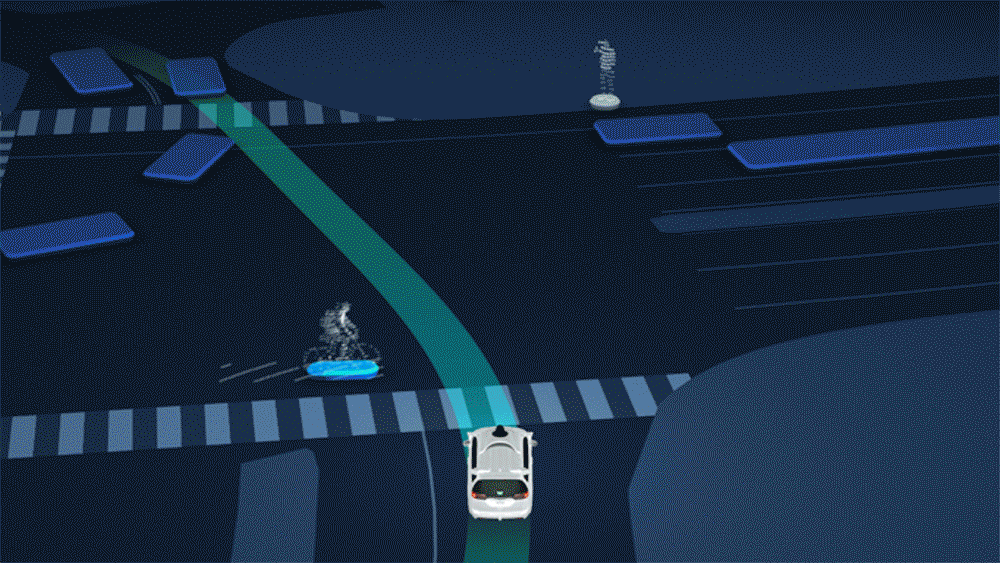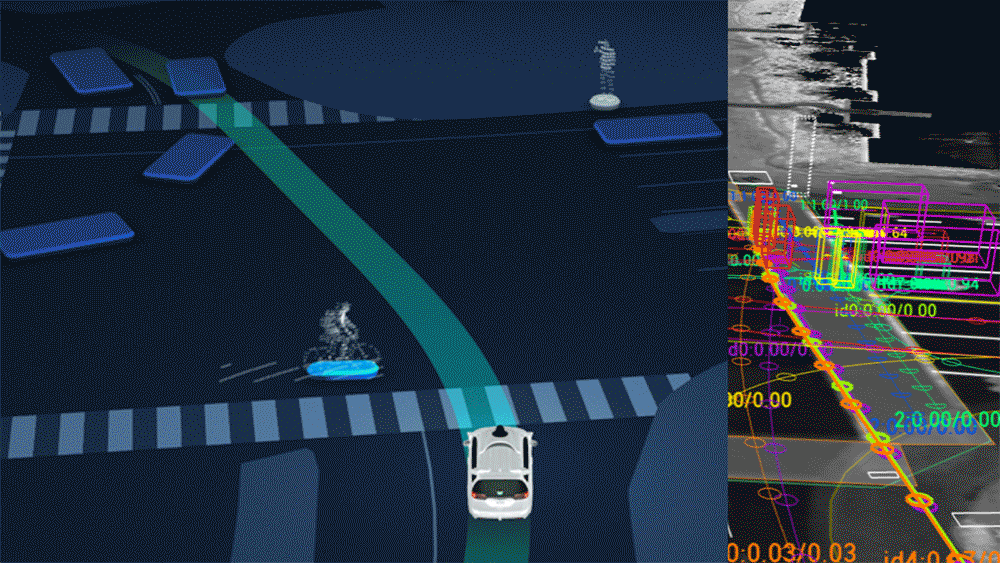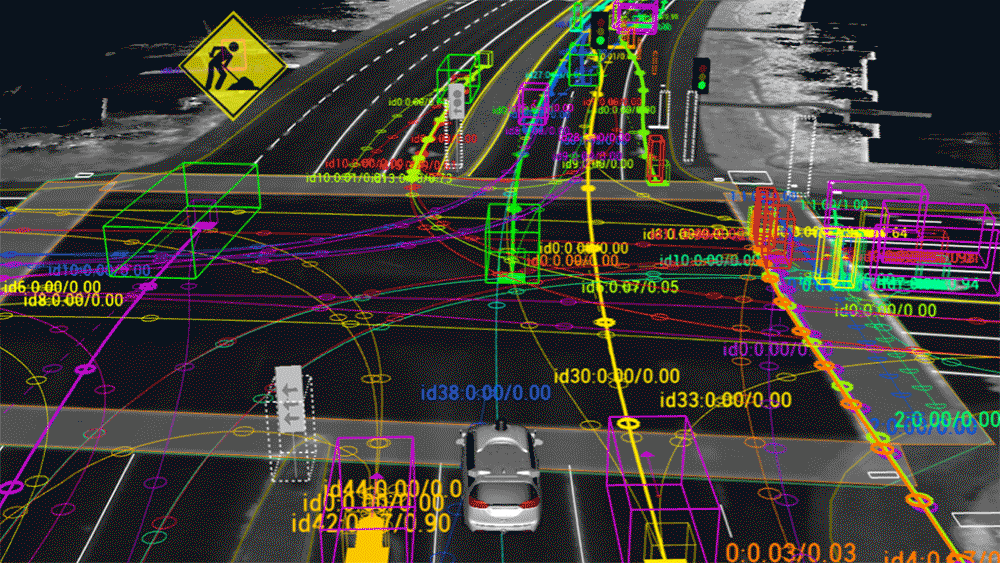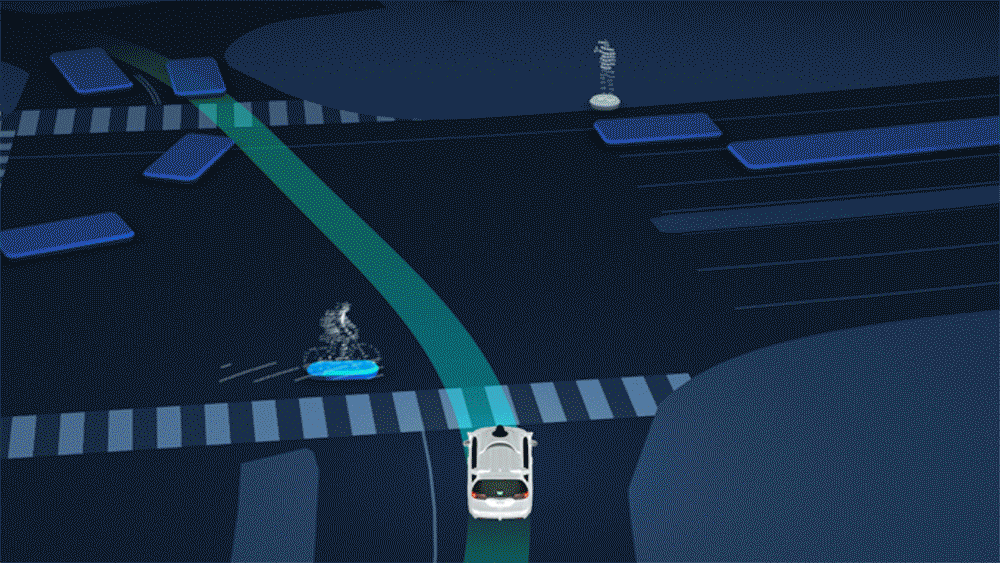
Independent Cars Data Rectangle Autonomous Car Data When individuals initially find out about the idea of self-sufficient vehicles, immediately, the vast majority of them intuit the framework’s extraordinary dependence on information.
The vehicle should be in steady correspondence with area following satellites, for example, and can send and get messages from different vehicles out and about.
Regardless of whether it’s to discover an objective or turn around a sudden impediment, everybody realizes that self-driving vehicles should be continually hoovering up information from the rest of the world, and regularly taking care of that information to cutting edge neural organization calculations to filter significance from it progressively.
In any case, however astounding as those outward capacities may be, what not many individuals acknowledge is that these vehicles may really accumulate the same amount of information from inside the vehicle as from outside of it. www.24x7offshoring.com
Travelers in the upcoming self-governing vehicles will be dependent upon the engaged consideration of a high level vehicular AI, and from multiple points of view the quality and welfare of their ride will be directed by the vehicle’s capacity to decipher human wishes and needs.
Conventional vehicles may run on gas, however self-governing vehicles run on information, and they’ll mine that information from anyplace they can.
Later on, you will converse with your vehicle
The most clear type of self-ruling vehicles information input is purposeful — voice orders.
This isn’t exactly just about as simple as it would appear, since right now practically the entirety of the discourse acknowledgment calculations require a cloud association with decipher sound at ongoing paces.
Voice control will at last transform the vehicle into the sans hands robot escort we’ve generally longed for, yet at present it’s simply too crude to even consider working as the essential type of vehicular control.
To satisfy the capability of the independent vehicle, we’ll need to improve either the speed and dependability of versatile information associations, or the speed and cost of incredible locally available vehicular PCs.
Fortunately, both of those figures are improving rapidly, alongside the productivity of the calculations being referred to.
This implies that soon proprietors of independent vehicles might say “take me home” to their dashboard, and have it recognize their ideal objective, however drive there minus any additional inquiry.
Further developed adaptations could even hear inferred orders, like the certain order to pivot inside the shout, “I failed to remember my wallet!”
www.24x7offshoring.com
With further developed, current discourse acknowledgment, vehicles could even figure out how to comprehend such upheavals through the slur of intoxication, making an evening to remember both more secure and more helpful.
Self-governing vehicles information will be mindful to words, yet activities too
Travelers in self-governing vehicles convey through more than their purposeful voice orders.
In actuality, compulsory correspondence may have similarly as a lot to show a vehicle what a traveler needs.
There are extraordinary models, for example, if a traveler loses consciousnesses and requirements the vehicle to settle all alone to set out toward an emergency clinic, however the utility of a mindful robot vehicle goes a long ways past wellbeing.
Adequately mindful programming could distinguish intoxication in a traveler and require self-heading to stay essentially, hence forestalling any driving while affected by inebriating substances — even those that can’t be recognized on a breathalyzer.
A vehicle could possibly see a traveler’s inclination for a marginally more slow, smoother ride to an objective, or it could see from their consistent looking at the time that they would favor a somewhat quicker, more forceful way through traffic.
And keeping in mind that vehicles will “learn” the most about best driving practices from searching externally at the vehicles around it, the responses of travelers inside (say, weariness at a sluggish turn or misery at a quick one) could advise its future conduct, too.
Self-ruling Cars Data – Garage
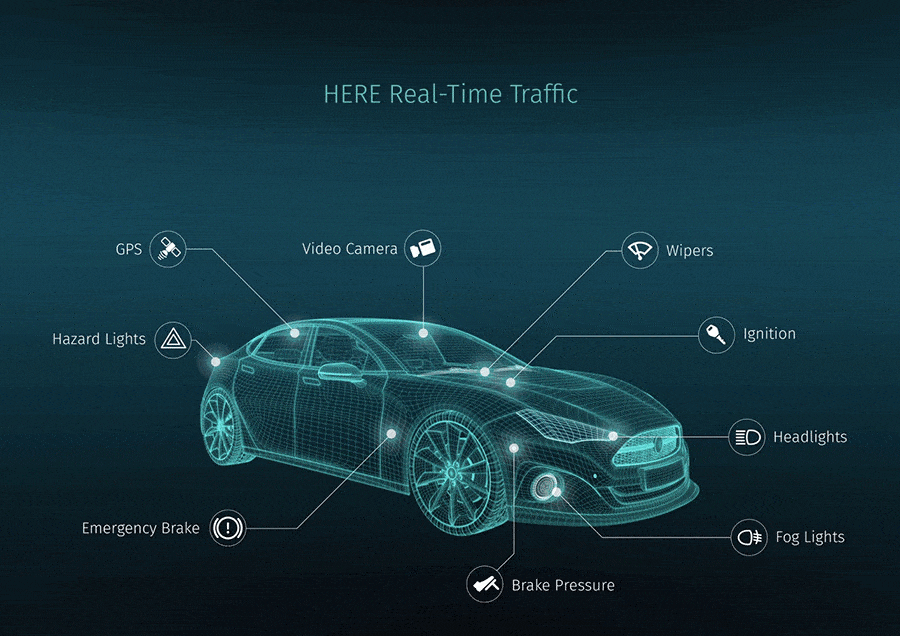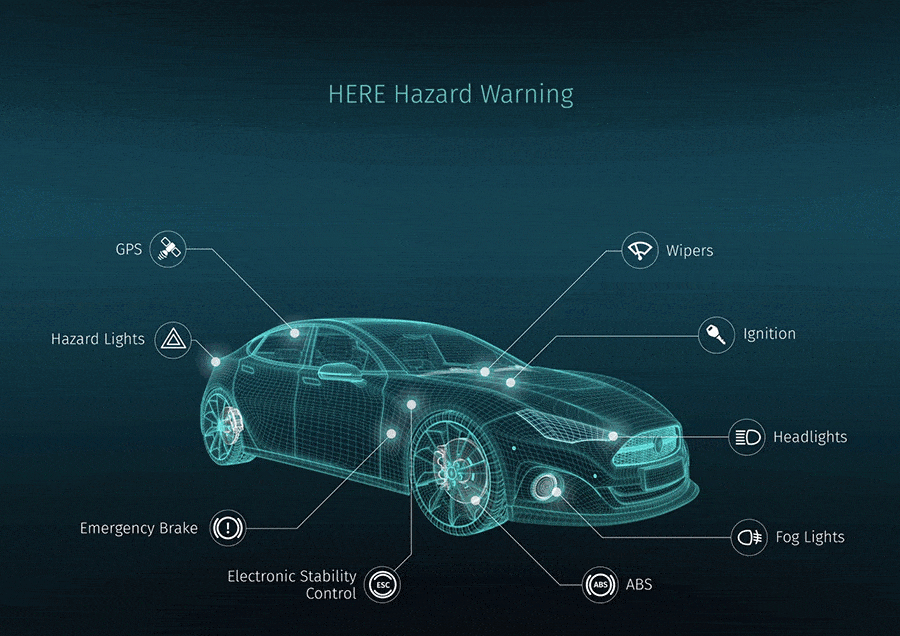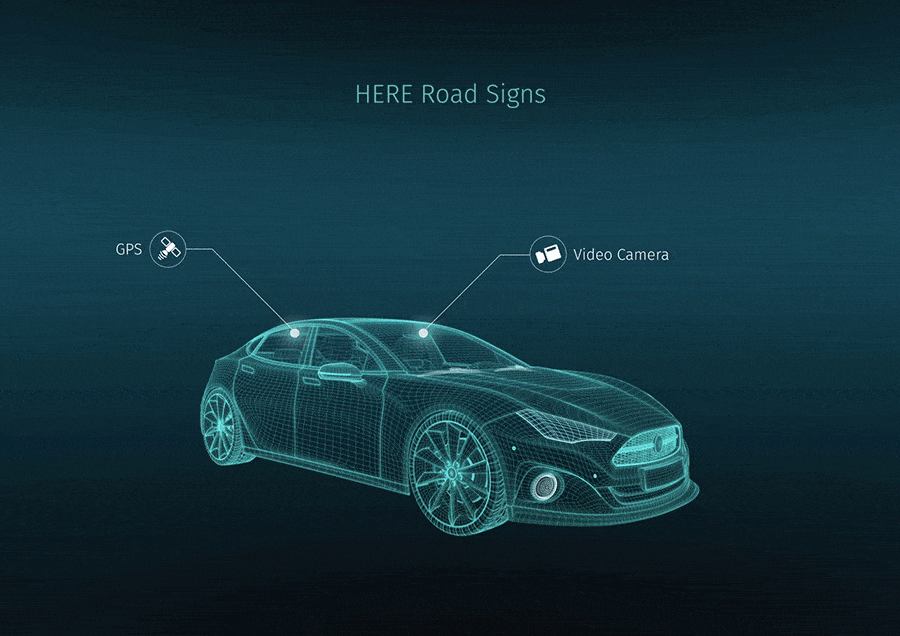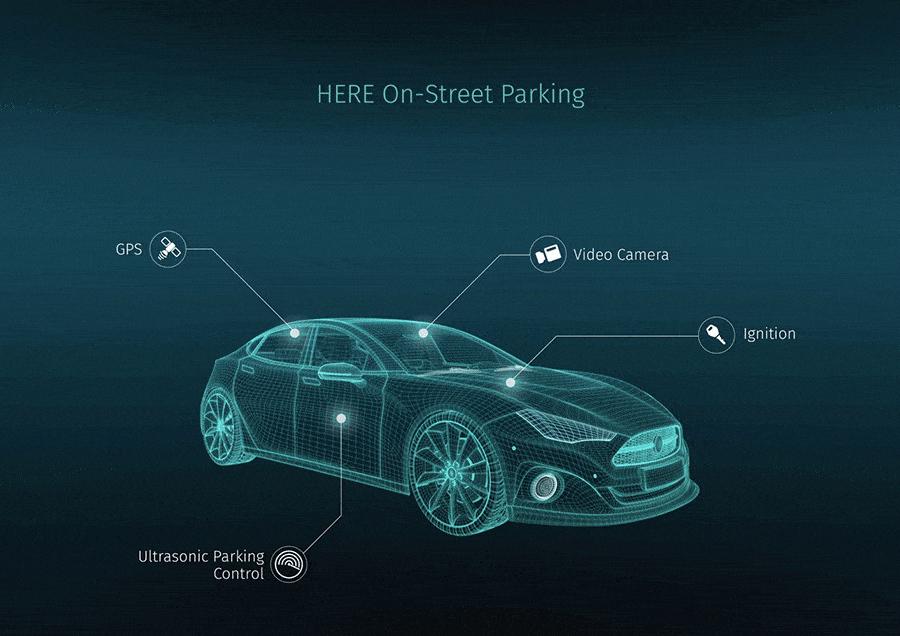
through Pexels
Self-rule implies arguing, too
A large portion of the correspondence among human and vehicle streams from the human to the vehicle — yet occasionally, the inverse is vital too.
Vehicles will for the most part advise travelers regarding relevant data without requiring a specific reaction, for example if there is a brief pause ahead because of rail vehicles passing.
The objective can be to just keep travelers educated, yet at different occasions the vehicle could think all the more effectively about other human necessities; realizing that a traveler is en route to a supermarket, it could recommend going to a nearer one simply a square from the vehicle’s present area. www.24x7offshoring.com
“Self-governing” vehicles will likewise at times need to request their travelers for bearing in the face from unrelated things choice focuses; confronted with a traffic reinforcement because of a fallen tree, should the vehicle go around for a speedier course home, or sit tight in line for lower gas utilization?
By posing such inquiries a couple of times, vehicles could develop a social profile for their proprietors, and settle on such choices all the more forcefully later on.
Such a favorable to dynamic information get-together could be similarly as essential to molding a vehicle’s conduct as any volume of driving information from the rest of the world.
Transform a vehicle ride into a short get-away
By both tuning in to a traveler and watching their conduct, vehicles ought to likewise have the option to extraordinarily improve the experience of traveling through traffic by fitting the experience.
Only one out of every odd traveler will need such a methodology, obviously, however those that do could have everything from the degree of outside commotion crossing out to the color of the windows to the point of the seat-back custom-made to their evident degree of stress.
An individual headed home with nothing else on the every day agenda may get an idea to stop for a treat in transit home, for example.
There are, obviously, still inquiries. It appears to be certain that exclusive vehicles would get their inclinations from their proprietors, however shouldn’t something be said about open vehicles like self-governing cabs?
On the off chance that there are different individuals in a self-driving vehicle, whose requirements ought to spur the vehicle’s activities?
Will it take a type of normal, or a dominant part rule approach?
Various administrators and even makers may wind up with various responses to these inquiries.
Every one of these thoughts require progresses in the information gathering equipment and information filtering programming that permits genuine comprehension of a human inhabitant, however it appears to be that there will be sufficient time for that advancement to occur.
That is on the grounds that none of the most eager applications for self-rule can be considered until self-driving vehicles can drive all over the place, with no human mediation at all.
That immensely significant capacity is as yet a reasonable distance out, implying that for the following quite a while the most imaginative personalities in tech will be laser centered around showing your vehicle how to gain from you.
There’s essentially no telling how far these inside information assortment innovations could progress or how self-sufficient vehicles information will work when they genuinely hit the street.
The Approach to Rule-Making: Normalization vs. Dominant Part Rule
Introduction: In the realm of rule-making, two distinct approaches are often considered: normalization and dominant part rule. These approaches reflect different philosophies and strategies in creating and implementing rules and regulations. In this article, we will explore these approaches and examine the benefits and considerations of each, shedding light on their implications for effective rule-making.
- Normalization Approach: The normalization approach to rule-making emphasizes creating a standardized framework where rules are designed to apply uniformly to all entities or individuals involved. This approach aims to establish a level playing field and ensure fairness and consistency in compliance and enforcement. Under the normalization approach, rules are developed based on broad consensus and commonly accepted practices, often incorporating input from various stakeholders.
Advantages of the Normalization Approach:
- Equality and Fairness: The normalization approach promotes equality by treating all entities or individuals in a similar manner. It reduces the potential for discrimination or bias in rule application and enforcement.
- Transparency: Standardized rules enhance transparency as they are readily accessible and applicable to everyone. This facilitates understanding, compliance, and dispute resolution.
- Efficiency: The normalization approach streamlines the rule-making process by adopting common rules across industries or sectors. This reduces duplication of efforts and resources required for creating and implementing specific rules for each entity or situation.
Considerations of the Normalization Approach:
- Lack of Flexibility: Standardized rules may not accommodate unique circumstances or specialized needs of certain entities or industries. This can limit innovation and adaptability, particularly in rapidly evolving sectors.
- Difficulty in Achieving Consensus: Developing rules based on broad consensus can be time-consuming and challenging, as different stakeholders may have conflicting interests or perspectives. This can slow down the rule-making process.
- Limited Local Contextualization: Rules developed through normalization may not adequately consider local cultural, social, or economic factors. This can lead to disconnects between the rules and the specific needs and dynamics of particular regions or communities.
- Dominant Part Rule Approach: The dominant part rule approach takes into account the prevailing practices or behaviors of the majority of entities or individuals within a specific industry or context. Under this approach, rules are designed based on the practices and standards already followed by the dominant players. The dominant part rule recognizes that the majority already adheres to certain norms, and rules are created to align with and reinforce those norms.
Advantages of the Dominant Part Rule Approach:
- Relevance and Adaptability: By aligning rules with prevailing practices, the dominant part rule approach ensures that rules remain relevant and adaptable to industry dynamics. This enables smoother compliance and minimizes disruptions.
- Industry Expertise: The dominant part rule approach leverages the expertise and knowledge of the dominant players, who often have extensive experience and insights into the industry. This enhances the practicality and effectiveness of the rules.
- Streamlined Implementation: Rules based on dominant practices are more likely to be readily accepted and implemented by the majority of entities or individuals. This reduces resistance and increases overall compliance.
Considerations of the Dominant Part Rule Approach:
- Potential for Exclusion: The dominant part rule approach may marginalize smaller or emerging players who do not conform to the practices of the dominant majority. This can stifle competition and limit opportunities for innovation and diversity within the industry.
- Risk of Entrenchment: Relying solely on dominant practices may hinder progress or change. It can discourage exploration of alternative approaches or discourage the adoption of new technologies or methodologies that have the potential to improve industry practices.
Conclusion: The choice between the normalization and dominant part rule approaches in rule-making depends on the specific context, goals, and dynamics of the industry or sector involved. While the normalization approach prioritizes fairness, consistency, and equality, the dominant part rule approach emphasizes relevance, adaptability, and industry expertise. Striking a balance between these approaches may be the key to effective rule-making, considering the need for fairness, innovation, and the ability to respond to industry dynamics. Ultimately, the optimal approach should seek to foster a robust and inclusive regulatory framework that supports industry growth, protects stakeholders’ interests, and serves the broader societal goals.
Determining the Approach: Normalization vs. Dominant Part Rule in Decision-Making
Introduction: In decision-making processes, it is crucial to select an appropriate approach to analyze and prioritize various options. Two common approaches used in decision-making are normalization and the dominant part rule. Each approach has its advantages and considerations depending on the specific context and goals of the decision. This article will explore the characteristics, applications, and considerations of both normalization and the dominant part rule to help guide decision-makers in choosing the most suitable approach.
Normalization Approach: The normalization approach involves assigning weights to different criteria or factors and calculating a normalized score for each option based on those weights. The scores are then compared to determine the best option. Here are some key aspects to consider when using the normalization approach:
Criteria Selection: Identify the relevant criteria that will influence the decision. These criteria can be qualitative or quantitative and should capture the key factors that impact the decision-making process. Examples could include cost, time, quality, customer satisfaction, or any other relevant factors.
Weight Assignment: Assign weights to each criterion to reflect its relative importance in the decision. The weights can be determined based on expert judgment, stakeholder preferences, or through a collaborative process. The sum of all weights should equal 1 to maintain consistency and ensure accurate normalization.
Data Collection: Collect data or information related to each criterion for all available options. This data could be obtained through surveys, measurements, historical records, or expert opinions. Ensure the data collected aligns with the specific criteria and is reliable and accurate.
Normalization: Normalize the data by transforming it to a common scale for comparison. This step involves applying mathematical transformations such as min-max scaling, z-score normalization, or other normalization techniques to ensure fairness in comparing different criteria.
Score Calculation: Calculate a normalized score for each option by multiplying the normalized values of the criteria by their corresponding weights and summing them up. The option with the highest score is considered the best choice.
Dominant Part Rule Approach: The dominant part rule approach is a simplified decision-making method that selects the option with the most favorable attributes or characteristics. This approach involves identifying a specific criterion or aspect that is considered the dominant part or the most important factor in the decision. Here are some considerations when using the dominant part rule approach:
Identifying the Dominant Part: Determine the specific criterion or attribute that holds the most significance in the decision-making process. This criterion could be based on the organization’s values, goals, or stakeholder preferences. It is crucial to clearly define and agree upon the dominant part before proceeding with the analysis.
Evaluation and Comparison: Evaluate each option based on the dominant part criterion. Determine which option performs the best or has the most favorable characteristics related to the dominant part. Compare the options and select the one that excels in the dominant part criterion.
Additional Considerations: While the dominant part rule focuses primarily on the dominant criterion, it is important to consider other relevant factors to avoid overlooking important aspects of the decision. Additional criteria or factors can be considered as secondary considerations, providing a more comprehensive evaluation of the options.
Stakeholder Alignment: Ensure that all stakeholders involved in the decision-making process are aligned and agree on the selection of the dominant part criterion. Open communication and consensus-building are essential to ensure the fairness and effectiveness of the decision.
Choosing the Appropriate Approach: The choice between normalization and the dominant part rule approach depends on the nature of the decision, the complexity of the criteria, and the specific requirements of the decision-makers. Here are some considerations for selecting the most suitable approach:
Decision Complexity: Normalization is often more appropriate when dealing with complex decisions that involve multiple criteria with varying degrees of importance. The normalization approach allows for a comprehensive evaluation of different criteria and their relative weights.
Data Availability and Reliability: Normalization requires a sufficient amount of reliable data for each criterion. If data is limited or unreliable, the dominant part rule approach may be more suitable, as it focuses on a single criterion or dominant attribute.
Decision Urgency: The dominant part rule approach is often quicker and simpler to implement compared to normalization, making it suitable for time-sensitive decisions where a quick and straightforward analysis is required.
Stakeholder Preferences: Consider the preferences and expectations of the stakeholders involved. If stakeholders value a more comprehensive analysis of multiple criteria, normalization may be preferred. On the other hand, if stakeholders prioritize specific attributes or have a clear dominant criterion in mind, the dominant part rule approach can be more suitable.
Conclusion: Both normalization and the dominant part rule are valuable decision-making approaches, each with its own merits and considerations. The choice between these approaches depends on factors such as decision complexity, data availability and reliability, decision urgency, and stakeholder preferences. By understanding the characteristics and applications of both approaches, decision-makers can select the most appropriate method to effectively analyze options and make informed decisions aligned with their goals and requirements.
Free Data Collection Resources Car Data

Searching for assets to help with gathering self-ruling vehicle information? Look at these supportive downloads:
The Ultimate Guide to Data Collection (PDF) – Learn how to gather information for arising innovation.
Eye Stare Sample Set (Download) – Get an example of excellent eye stare information.
Street, Car, and People Dataset (Download) – Training a framework that requires street picture information? Download our example dataset.
Need assistance building up a custom dataset? Globalme gives custom video and picture information assortment administrations to prepare your self-driving vehicle AI.
Visit with us about energizing your self-sufficient vehicle innovation with excellent datasets
Self-sufficient Cars Data RectangleWhen individuals initially find out about the idea of self-ruling vehicles, immediately, the greater part of them intuit the framework’s unimaginable dependence on information.
The vehicle should be in steady correspondence with area following satellites, for example, and can send and get messages from different vehicles out and about.
Regardless of whether it’s to discover an objective or turn around a startling hindrance, everybody realizes that self-driving vehicles should be continually hoovering up information from the rest of the world, and frequently taking care of that information to cutting edge neural organization calculations to filter importance from it continuously.
All things considered, however astonishing as those outward capacities seem to be, what not many individuals acknowledge is that these vehicles may really assemble the same amount of information from inside the vehicle as from outside of it. www.24x7offshoring.com
Travelers in the upcoming independent vehicles will be dependent upon the engaged consideration of a high level vehicular AI, and from various perspectives the quality and wellbeing of their ride will be directed by the vehicle’s capacity to decipher human wishes and needs.
Conventional vehicles may run on gas, yet self-sufficient vehicles run on information, and they’ll mine that information from anyplace they can.
Later on, you will converse with your vehicle
The most clear type of self-ruling vehicles information input is deliberate — voice orders.
This isn’t exactly just about as simple as it would appear, since right now practically the entirety of the discourse acknowledgment calculations require a cloud association with interpret sound at ongoing velocities.
Voice control will at last transform the vehicle into the sans hands robot driver we’ve generally longed for, however at present it’s simply too crude to even think about working as the essential type of vehicular control.
To satisfy the capability of the self-governing vehicle, we’ll need to improve either the speed and dependability of versatile information associations, or the speed and cost of amazing installed vehicular PCs.
Fortunately, both of those figures are improving rapidly, alongside the effectiveness of the calculations being referred to.
This implies that soon proprietors of self-governing vehicles might say “take me home” to their dashboard, and have it distinguish their ideal objective, however drive there minus any additional inquiry.