The Carolina Algonquians were a Native American tribe that inhabited the coastal regions of what is now North Carolina. They had their own unique language, which was a member of the Algonquian language family. Unfortunately, like many indigenous languages, the Carolina Algonquian language has been lost over time due to colonization and cultural assimilation. However, there is a growing movement to rediscover and revive these endangered languages, recognizing their importance in preserving cultural heritage and promoting linguistic diversity.
Preserving and reviving endangered languages is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, language is an integral part of a community’s identity and culture. It carries with it the history, traditions, and knowledge of a people. When a language becomes extinct, a significant part of that community’s heritage is lost forever. Secondly, linguistic diversity is essential for maintaining a healthy global society. Each language offers unique perspectives and ways of understanding the world. By preserving endangered languages, we ensure that this diversity is maintained and celebrated.
Key Takeaways
- Rediscovering the lost language of the Carolina Algonquians is crucial for preserving Native American history.
- The Algonquian language played a significant role in the culture and traditions of Native American tribes.
- Translating the Algonquian language poses challenges due to linguistic and cultural barriers.
- Language translators and experts play a vital role in accurately interpreting and translating the Algonquian language.
- Translation software and tools, as well as outsourcing translation services, can help make the translation process more efficient and accurate.
Understanding the Carolina Algonquians Language and Its Significance in Native American History
The Algonquian language family is one of the most widespread language families in North America. It includes numerous dialects and languages spoken by various Native American tribes across the continent. The Carolina Algonquian language was one such dialect within this family.
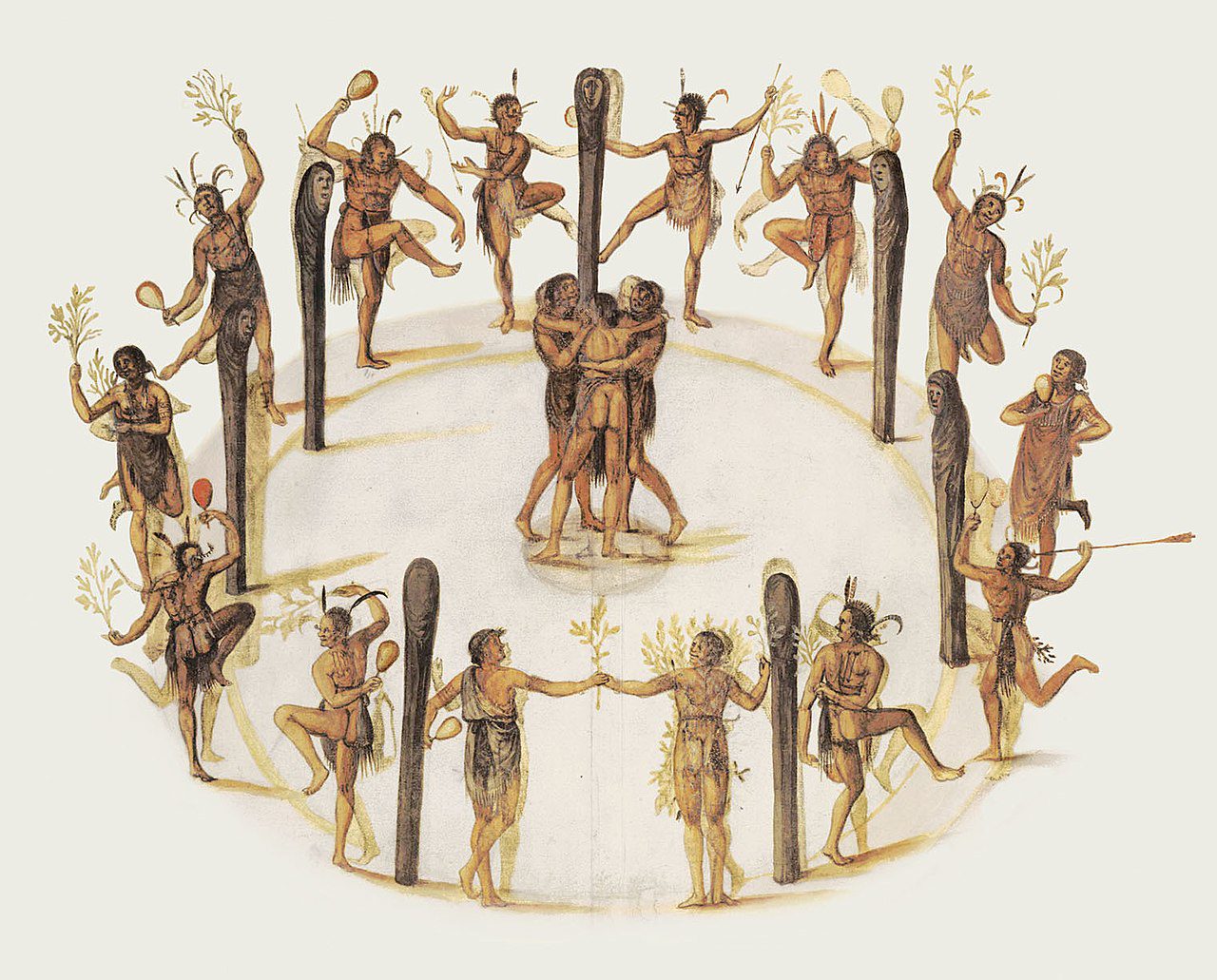
The significance of the Algonquian language in Native American history cannot be overstated. It was not only a means of communication but also a vehicle for transmitting cultural knowledge, stories, and traditions from one generation to another. The language reflected the unique worldview and cosmology of the Carolina Algonquians, providing insights into their spiritual beliefs, social structures, and daily life.
Challenges in Translating the Algonquian Language: Overcoming Linguistic and Cultural Barriers
Translating the Algonquian language presents several challenges, primarily due to the linguistic and cultural barriers that exist. Firstly, there are limited resources available for studying and understanding the language. Many of the original speakers of the Carolina Algonquian language have passed away, leaving behind only fragmentary records and documents. This scarcity of resources makes it difficult to reconstruct the language accurately.
Secondly, cultural differences can pose challenges in translation. Language is deeply intertwined with culture, and certain concepts or expressions may not have direct equivalents in other languages. Translators must navigate these cultural nuances to ensure accurate and meaningful translations.
To overcome these challenges, linguists and researchers rely on a combination of methods, including comparative linguistics, historical records, and collaboration with Native American communities. By working closely with community members who have knowledge of their ancestral language and culture, linguists can gain valuable insights and ensure that translations are culturally sensitive and accurate.
Language Translators: The Role of Experts in Translating and Interpreting the Algonquian Language
| Metrics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of Algonquian languages | 30 |
| Number of Algonquian speakers | Less than 10,000 |
| Number of Algonquian language experts | Unknown |
| Number of Algonquian language interpreters | Unknown |
| Number of Algonquian language translators | Unknown |
| Challenges faced by Algonquian language translators | Lack of resources, limited vocabulary, complex grammar |
| Importance of Algonquian language translators | Preservation of culture, communication with non-speakers, access to education and healthcare |
The role of experts in translating and interpreting the Algonquian language cannot be overstated. These individuals possess a deep understanding of the language’s grammar, vocabulary, and cultural context. They are able to bridge the gap between the original language and the target language, ensuring that translations are accurate and meaningful.
Effective translation requires more than just fluency in both languages. Translators must also possess a deep knowledge of the subject matter being translated. In the case of Algonquian language translation, this includes an understanding of Native American history, culture, and traditions. This expertise allows translators to capture the nuances and subtleties of the original text, ensuring that nothing is lost in translation.
Translate with Ease: The Advantages of Using Translation Software and Tools
Translation software and tools can be invaluable resources for translating the Algonquian language. These tools utilize machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence to automate the translation process, making it faster and more efficient.
One of the main advantages of using translation software is its ability to handle large volumes of text. For projects that involve translating extensive documents or archives, manual translation can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Translation software can process large amounts of text in a fraction of the time, allowing for quicker turnaround times and increased productivity.
Additionally, translation software can help maintain consistency in translations. It can create glossaries and translation memories, which store previously translated terms and phrases. This ensures that translations are consistent across different documents and projects, maintaining accuracy and quality.
24x7offshoring: Outsourcing Translation Services to Meet the Demands of the Project

For larger projects that require extensive translation work, outsourcing translation services can be a practical solution. Companies like 24x7offshoring specialize in providing professional translation services for a wide range of languages, including Algonquian.
Outsourcing translation services offer several benefits. Firstly, it allows organizations to tap into a global network of translators who possess expertise in specific languages and subject matters. This ensures that translations are accurate and culturally sensitive.
Secondly, outsourcing translation services can help meet tight deadlines and manage fluctuating workloads. Professional translation companies have the resources and infrastructure to handle large volumes of work efficiently, ensuring that projects are completed on time.
From Audio to Text: The Importance of Transcription in Language Translation
Transcription plays a crucial role in language translation, especially when dealing with audio or video recordings. Transcribing spoken language into written form allows translators to work with the text more easily and accurately.
In the case of the language, transcription is particularly important due to the scarcity of written resources. Many records and documents are in audio or video format, requiring transcription before they can be translated.
Transcription also helps in preserving and archiving the language for future generations. By transcribing spoken recordings, linguists can create written records that can be studied and analyzed, contributing to the ongoing efforts to revive and preserve endangered languages.
Translation Services: Finding the Right Provider for Accurate and High-Quality Translations
When choosing a translation service provider for Algonquian language translation, several factors should be considered. Firstly, it is essential to ensure that the provider has expertise in the specific language and subject matter. This can be determined by reviewing their portfolio, client testimonials, and certifications.
Secondly, reliability and accuracy are crucial. Look for a provider that has a reputation for delivering high-quality translations within the agreed-upon deadlines. It is also helpful to inquire about their quality assurance processes, such as proofreading and editing.
Lastly, consider the provider’s approach to cultural sensitivity. Translation is not just about converting words from one language to another; it is about conveying meaning and preserving cultural nuances. A reliable translation service provider will prioritize cultural sensitivity and work closely with Native American communities to ensure accurate and respectful translations.
AI and Language Translation: How Artificial Intelligence is Revolutionizing the Translation Industry
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the translation industry, offering new possibilities for language translation. AI-powered translation tools utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data and improve translation accuracy over time.
One of the main benefits of AI-powered translation tools is their ability to handle complex linguistic structures and nuances. These tools can analyze sentence structure, grammar rules, and idiomatic expressions, resulting in more accurate translations.
AI-powered translation tools also offer real-time translation capabilities, making them useful for live interpretation or communication with non-native speakers. They can instantly translate spoken or written language, facilitating cross-cultural communication and understanding.
Data Collection and Preservation: The Importance of Documenting and Archiving the Algonquian Language for Future Generations
Documenting and archiving the Algonquian language is crucial for preserving it for future generations. Efforts to collect and record the language ensure that it is not lost forever and can be studied and revitalized.
One of the main challenges in documenting endangered languages like Algonquian is the scarcity of resources. Many records and documents have been lost or destroyed over time. However, ongoing efforts are being made to collect and digitize existing materials, such as audio recordings, written documents, and oral histories.
Archiving the Algonquian language also involves creating accessible resources for researchers, linguists, and community members. This can include online databases, dictionaries, grammar guides, and educational materials. By making these resources available, we can ensure that the language remains alive and accessible to future generations.
In conclusion, rediscovering and reviving the lost language is of utmost importance. Preserving endangered languages like Algonquian is crucial for maintaining cultural heritage, promoting linguistic diversity, and fostering cross-cultural understanding.
By overcoming linguistic and cultural barriers, utilizing translation software and tools, outsourcing translation services when necessary, transcribing audio recordings, finding reliable translation service providers, harnessing the power of AI in translation, and documenting and archiving the language for future generations, we can ensure that the rich linguistic heritage of the Carolina Algonquians is not lost but celebrated and cherished.
If you’re interested in the language, you may also find this article on the importance of data labeling intriguing. Data labeling plays a crucial role in various fields, including language preservation and translation. Check out the article here to learn more about how data labeling can contribute to the preservation and understanding of languages like Carolina Algonquian.
FAQs
What is the Language?
The Carolina Algonquian Language is an extinct Algonquian language that was spoken by the Carolina Algonquian people who lived in what is now North Carolina, South Carolina, and Virginia.
When was t Language spoken?
The Carolina Algonquian Language was spoken from around 500 AD to the late 18th century.
Why did the Language become extinct?
The Carolina Algonquian Language became extinct due to a combination of factors, including disease, warfare, and forced assimilation into European culture.
Is there anyone who still speaks t Language?
No, there are no known speakers of the Carolina Algonquian Language today.
What is known about the grammar and vocabulary of the Language?
Some information about the grammar and vocabulary Language has been preserved through written records and the study of related Algonquian languages. However, much of the language remains unknown.
What impact did the have on other languages?
The Carolina Algonquian Language had a significant impact on the English language, as many words from the language were adopted into English, including “tomahawk,” “moccasin,” and “papoose.”
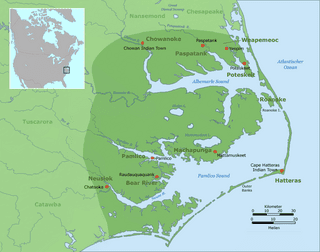
Carolina Algonquian (also known as Pamlico, Croatoan) was an Algonquian language of the Eastern Algonquian subgroup formerly spoken in North Carolina, United States. Carolina Algonquian was formerly spoken by Secotan (later known as Machapunga), Chowanoke and Weapemeoc (subgroups Poteskeit and Paspatank) peoples.
In 1584 Sir Walter Raleigh had dispatched the first of a number of expeditions to Roanoke Island to explore and eventually settle the New World. Early encounters with the natives were friendly, and, despite the difficulties in communication, the explorers were able to persuade “two of the savages, being lustie men, whose names were Wanchese and Manteo” to accompany them on the return voyage to London, in order for the English people to report both the conditions of the New World that they had explored and what the usefulness of the territory might be to the English.
Once safely delivered to England, the two Indians quickly made a sensation at court. Raleigh’s priority, however, was not publicity but rather intelligence about his new land of Virginia, and he restricted access to the exotic newcomers, assigning the brilliant scientist Thomas Harriot the job of deciphering and learning the Carolina Algonquian language, using a phonetic alphabet of his own invention in order to effect the translation.
