HUMAN IN THE LOOP
https://24x7offshoring.com/
http://24x7outsourcing.com/
What is Human-tuned in Machine Learning or Human In The Loop?
Human-on top of it (HITL) is a part of man-made brainpower that use both human and machine knowledge to make AI models. In a conventional human-on top of it approach, individuals are associated with an idealistic circle where they train, tune, and test a specific calculation.
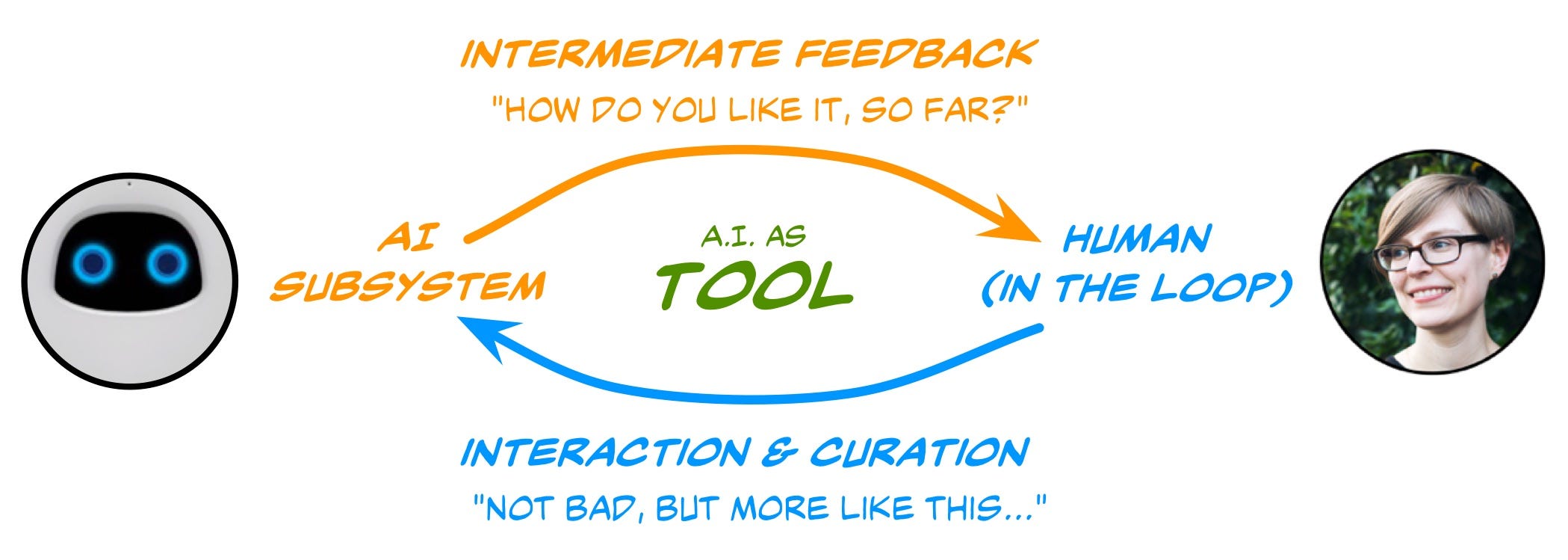
By and large, it works this way:
To begin with human in the loop , people mark information. This gives a model superior grade (and high amounts of) preparing information. An AI calculation figures out how to settle on choices from this information.
Then, people tune the model. This can be 24x7offshoring.com in a few distinct manners, however regularly, people will score information to represent over fitting, to show a classifier edge cases, or new classifications in the model’s domain.
Ultimately, individuals can test and approve a model by scoring its yields, particularly in places where a calculation is unconfident about a judgment or excessively certain about an off base choice.
Presently, it’s essential to take note of that every one of these activities includes a consistent input circle.
Human-tuned in AI implies taking every one of these preparation, tuning, and testing errands and taking care of them back into the calculation so it gets more astute, more certain, and more exact.
This can be particularly successful when the model chooses what it needs to realize next–known as dynamic learning–and you send that information to human annotators for preparing.
Human-insider savvy is a methodology that we at 24x7offshoring.com have advocated for quite a long time.
We’ve seen it help improve models of each stripe, regardless of whether they’re text classifiers, PC vision calculations, or search and data recovery models.
We can make tremendous amounts of exceptionally exact preparing information for your special use case, at that point tune your model with human understanding, and test it to settle on sure its choices are precise and significant.
In the event that you’d prefer to find out additional, kindly don’t stop for a second to connect.
Human-in the know FAQs
How would you consolidate individuals and machines to make computer based intelligence?
The human-in the know approach consolidates the best of human insight with the best of machine insight. Machines are perfect at settling on savvy choices from tremendous datasets, while individuals are vastly improved at pursuing choices with less information.For model, individuals are perfect at checking out at a perplexing picture and selecting discrete substances: “this is a light post” or “that is a feline, yet you can see its tail.” This is the specific kind of data a machine needs to comprehend what a light post or a feline resembles. As a matter of fact, a machine needs to see a variety of light posts and felines from various points, to some extent impeded, in various varieties, and so on to comprehend what one resembles. A vigorous dataset of these marked pictures (for example human knowledge) trains a machine to see those things (for example machine insight). Furthermore, sooner or later, with enough information and enough tuning, those machine calculations can see and comprehend pictures rapidly and unquestionably precise without the requirement for individuals to continually tell it what precisely a feline (or a light post) seems to be.
The Human in the Loop: Empowering AI with Human Intelligence
As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to advance, the concept of “human in the loop” has emerged as a crucial approach to harnessing the combined power of machines and human intelligence. By integrating human expertise and decision-making into AI systems, the human in the loop model ensures the accuracy, fairness, and ethical considerations necessary for effective and responsible AI applications.
Understanding the Human in the Loop Model:
The human in the loop model refers to a collaborative framework where humans play an active role in AI systems. Unlike fully automated AI processes, the human in the loop approach incorporates human oversight, intervention, and decision-making at various stages of AI development and deployment. This collaboration between humans and machines aims to enhance AI capabilities, address limitations, and ensure the desired outcomes.
Benefits of Human in the Loop:
Improved Accuracy and Quality:
Human involvement in AI systems can significantly improve accuracy and quality. Humans can provide contextual understanding, interpret ambiguous situations, and make informed judgments that may be challenging for AI algorithms alone. By combining human intelligence with AI automation, errors can be minimized, and the overall performance of the system can be enhanced.
Ethical Considerations and Fairness:
AI systems must adhere to ethical guidelines and ensure fairness in their decision-making processes. The human in the loop model allows human experts to evaluate and correct biases or discriminatory outcomes that AI algorithms may produce. Human intervention ensures that AI technologies align with societal values, promoting fairness and preventing unintended harm.
Adaptability and Learning:
Humans possess the ability to adapt, learn, and acquire new knowledge based on changing circumstances. By incorporating human feedback into AI systems, algorithms can be continuously improved and updated to address emerging challenges or evolving user needs. The human in the loop model allows for ongoing learning and iterative refinement of AI solutions.
Challenges of Human in the Loop:
Time and Cost:
Involving humans in AI systems can be time-consuming and costly. Human input requires resources, including expertise, training, and labor. Balancing the efficiency of AI automation with the need for human involvement is a challenge that organizations must navigate to optimize the human in the loop model.
Human Bias and Subjectivity:
Humans are susceptible to bias and subjectivity, which can inadvertently influence the decisions made within the human in the loop model. Bias awareness and training are essential to ensure that human judgment is fair, unbiased, and consistent across different scenarios. Careful selection and diverse representation of human contributors can help mitigate biases.
Scalability and Real-Time Decision-Making:
As AI systems operate at scale and in real-time, involving humans in every decision can become impractical or inefficient. Striking a balance between human oversight and the need for timely automated decisions is crucial. Identifying when human input is most valuable and designing systems accordingly is key to addressing this challenge.
The Future of Human in the Loop:
The human in the loop model is expected to play an increasingly important role in AI development and deployment. As AI technologies advance, the integration of human expertise and oversight becomes vital for ensuring responsible and ethical AI applications. The future of human in the loop lies in refining the collaboration between humans and machines, leveraging the unique strengths of each to achieve optimal results.
The human in the loop model represents a powerful paradigm for AI development and deployment. By combining human intelligence, ethical considerations, and adaptability with AI automation, this model empowers AI systems to achieve higher accuracy, fairness, and effectiveness. While challenges such as bias, scalability, and cost exist, the benefits of human in the loop are clear. As AI continues to shape various aspects of our lives, the human in the loop approach will play a crucial role in ensuring AI technologies align with human values, address societal concerns, and drive positive impact.
When would it be advisable for you to involve human-in the know AI?
For preparing: As we talked about above, people can be utilized to give named information to demonstrate preparing. This is likely the most well-known place you’ll see information researchers utilize a HitL approach.
For tuning or testing: People can likewise assist with tuning a model for higher precision. Say your model is unconfident about a specific arrangement of choices, as in the event that a specific picture is as a matter of fact a feline. Human annotators can score those choices, successfully telling the model, “indeed, this is a feline” or “no, it’s a light post,” consequently tuning it so it’s more exact from now on.

What’s the contrast between human-in the know and dynamic learning?
Dynamic advancing by and large alludes to the people dealing with low certainty units and taking care of those back into the model. Human-in the know is more extensive, enveloping dynamic learning approaches as well as the production of informational indexes through human naming. Furthermore, HitL can at times (however seldom) allude to individuals essentially approving (or discrediting) a result without taking care of those decisions back to the model.
Who involves human-in the know AI?
HitL can and is utilized for complex man-made intelligence projects. This incorporates NLP, PC vision, feeling examination, record, and a huge measure of other use cases. Any profound gaining computer based intelligence can profit from some human knowledge embedded into the circle sooner or later.
Human in the Loop: Unleashing the Power of Human-AI Collaboration
In today’s era of rapid technological advancements, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool that promises to revolutionize various industries and sectors. However, as AI systems become more sophisticated, there is a growing recognition of the importance of human involvement in the decision-making process. This is where the concept of “Human in the Loop” comes into play
Understanding Human in the Loop:
Human in the Loop refers to a collaborative approach that integrates human judgment, oversight, and decision-making into AI systems. Instead of relying solely on automated processes, Human in the Loop recognizes the valuable role that humans can play in refining, validating, and enhancing AI algorithms and outputs. By incorporating human input at various stages of the AI lifecycle, organizations can achieve more accurate, transparent, and ethically responsible outcomes.
Applications in Various Domains:
Human in the Loop methodology finds applications in a wide range of domains, including healthcare, finance, customer service, and autonomous systems. In healthcare, for instance, AI-powered diagnostic tools can be enhanced by involving medical professionals to validate and interpret results. In finance, human oversight helps ensure compliance, identify anomalies, and make informed decisions. Customer service chatbots can benefit from human intervention to handle complex queries and provide personalized support. Even in autonomous systems like self-driving cars, human monitoring remains essential for safety and handling unpredictable situations.
Benefits of Human in the Loop:
a. Improved Accuracy: Human oversight allows for error detection, correction, and refinement of AI models, leading to improved accuracy and reliability of results.
b. Ethical Considerations: Humans can provide the necessary ethical judgment to ensure that AI systems align with societal values, avoiding biased or discriminatory outcomes.
c. Complex Problem-Solving: AI systems often struggle with handling complex and ambiguous scenarios. Human involvement can provide context, common sense reasoning, and creative problem-solving abilities.
d. Adaptability and Learning: Humans can adapt and learn from new situations and changing environments, making them valuable in addressing evolving challenges that AI may not anticipate.
Challenges of Human in the Loop:
a. Time and Cost: Human involvement in the loop can increase time and resource requirements, especially for tasks that demand extensive human input.
b. Human Bias: Human biases can inadvertently influence the decision-making process, potentially affecting the objectivity and fairness of AI systems.
c. Scalability: Integrating human oversight at scale can be challenging, particularly in scenarios with large volumes of data or real-time decision-making requirements.
Ensuring Effective Human in the Loop Collaboration:
To harness the full potential of Human in the Loop, organizations must establish clear guidelines and frameworks:
a. Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Define the roles of humans and AI systems, ensuring transparency and accountability.
b. Training and Expertise: Provide adequate training to humans involved in the loop, enabling them to understand AI systems, their limitations, and potential biases.
c. Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms for continuous feedback and communication between humans and AI systems to facilitate mutual learning and improvement.
d. Ethical Guidelines: Develop ethical frameworks to guide human-AI collaboration, promoting fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Human in the Loop represents a paradigm shift in the development and deployment of AI systems. By acknowledging the importance of human judgment, expertise, and ethics, organizations can harness the strengths of both humans and AI to achieve more accurate, reliable, and ethical outcomes. Human in the Loop collaboration empowers us to shape the future of AI, ensuring that technology remains a tool for augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them. As we navigate the exciting possibilities of AI, embracing a human-centered approach will be crucial in creating a better and more inclusive future for all.
The Power of Human in the Loop: Enhancing Artificial Intelligence with Human Intelligence
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence (AI), the concept of “human in the loop” has emerged as a crucial component for optimizing AI systems. As AI technologies continue to advance, it becomes apparent that humans bring unique cognitive abilities and contextual understanding that complement the computational power of machines. In this article, we will delve into the significance of human in the loop, exploring its benefits and how it enhances the capabilities of AI systems.
Human in the loop refers to the integration of human intelligence and expertise into the AI development and deployment process. By involving humans alongside AI algorithms, organizations can ensure more accurate, reliable, and contextually appropriate outcomes. This collaborative approach combines the strengths of humans, such as reasoning, judgment, and creativity, with the computational capabilities of AI systems.

One area where human in the loop proves invaluable is in data annotation and validation. AI algorithms heavily rely on labeled data for training, and humans play a vital role in annotating and verifying the accuracy of the datasets. By incorporating human judgment and expertise, organizations can ensure that the training data is representative and free from biases, leading to more reliable AI models.
In complex decision-making scenarios, human in the loop becomes essential. While AI systems excel at processing vast amounts of data, they often struggle with contextual understanding and ethical considerations. Humans bring valuable insights and the ability to consider factors beyond data, such as cultural norms, emotions, and subjective judgments. Incorporating human judgment helps address ethical concerns and ensures that AI decisions align with societal values and norms.
Ambiguity and uncertainty are inherent in many real-world situations. AI systems can struggle to handle such scenarios with absolute accuracy. Human in the loop allows humans to provide clarification, disambiguation, and additional information that enhances the AI’s understanding and decision-making capabilities. Humans can also navigate situations where interpretation and subjective judgment are required, improving the overall accuracy and relevance of AI outputs.
The continuous learning and improvement of AI systems are facilitated by human in the loop. Humans can identify shortcomings, refine algorithms, and update training data based on new insights and emerging trends. This iterative process ensures that AI models remain up to date and adaptable to changing circumstances.
Benefits of human in the loop are numerous. It enhances the accuracy and reliability of AI systems by incorporating human oversight and validation. Humans can catch and correct errors, ensuring that AI-generated results are trustworthy. Furthermore, involving humans in the decision-making process promotes ethical and responsible AI practices. Humans can identify potential biases, ethical dilemmas, and unintended consequences that AI algorithms might overlook, leading to fairer and more accountable AI systems.
The user experience is also improved through human in the loop. Humans can provide nuanced feedback, preferences, and individual insights that help AI applications deliver personalized experiences. By understanding user needs and preferences, AI systems can adapt and evolve to meet their requirements, resulting in higher user satisfaction and engagement.
Flexibility and adaptability are additional advantages of human in the loop. Humans bring the ability to recognize new patterns, emerging trends, and anomalies that AI algorithms may not detect. By integrating human expertise, AI systems can remain versatile and effective in dynamic environments, adapting to changing circumstances and handling novel situations.
In conclusion, human in the loop represents a fundamental shift in the development and application of AI. By leveraging human intelligence, expertise, and judgment, AI systems can overcome limitations and deliver more accurate, reliable, and responsible outcomes. The integration of humans into the AI loop enhances decision-making, addresses ambiguity and uncertainty, and promotes ethical practices. As AI continues to progress, human in the loop will play a pivotal role in unlocking the true potential of this transformative technology, enabling a future where humans and machines collaborate synergistically to achieve remarkable advancements across various domains.

