What is the function of a translator?
What is a translator?
A translator is a professional who specializes in changing written or spoken material from one language to another while maintaining the unique meaning, design, and tone. They play a vital role in facilitating conversation and experience between exceptional language audio systems.
What does a translator do?
A translator reads and understands given material, researches accurate business terminology, and uses specialized dictionaries and translation equipment to transform text and audio recordings from one language to one or more. They ensure that translated content correctly conveys authentic meaning and tone. Additionally, translators review and edit their work, collaborate with group participants and clients, and stay updated live on new translation equipment and practices.
The translator’s obligations include:
- analyze the material and discover company-specific terminology
- convert text and audio recordings in one language to one or more languages
- ensure that translated texts convey authentic meaning and tone
- activity summary
As a translator, your obligations will include carefully reading and understanding the context of the material provided, using specialized dictionaries and translation equipment, and meticulously reviewing the latest translations. Success in this position requires excellent attention to detail and fluency in at least additional languages in addition to his native tongue.

Your number one goal will be to offer translated content that aligns with our internal needs and allows us to efficiently interact with a broader target market.
If you have strong language skills and are passionate about the language, we encourage you to join our group as we try to bridge the gaps in conversation and foster multilingual knowledge.
Obligations
- Examine the given fabric and research the company’s unique terminology.
- Convert text and audio recordings from one language to one or more others
- Ensure that translated content conveys the original meaning and tone.
- Create subtitles for movies and shows online
- Cross references specialized dictionaries and translation teams to test the quality of the translation
- Review translated texts for accuracy of grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Follow up with the group’s internal collaborators and with clients to ensure that the translation meets their wishes.
- Edit the content to maintain its unique design (for example, font and structure).
- Red with field. experts to stay up to date with new translation equipment and practices,
- Requirements and capabilities , confirmed job, enjoy as a translator, interpreter or similar role,
- Fluency in at least two languages, as well as your native language,
- Splendid proofreading skills with the ability to find grammar, spelling and punctuation errors.
- Desirable information about the team to improve the content.
- Familiarity with translation software.
- Time management skills.
- Bachelor’s degree in translation, decoding or similar discipline. A
- Additional certification in linguistics is a plus.
The translator’s motive
Interpret a high-level language application directly into a machine language application that the central processing unit (CPU) can understand. It also detects errors in the software.
Unique varieties of translators.
There are three unique types of translators, the following:
Compiler
A compiler is a translator used to convert a high-level programming language into a low-level programming language. Convert all software in a single query and check for errors detected after conversion. The compiler takes time to do its job by translating high-level code into lower-level code and then storing it in memory.
A compiler is established by the processor and based on a platform. but it has been fixed by special compiler, go compiler and source to source compiler. Before choosing a compiler, the user must first understand the training set architecture (ISA), the operating system (OS), and the programming language to be used to ensure it is compatible.
An interpreter
Similar to a compiler it is a translator that is used to convert a high stage programming language into a low stage programming language. Convert the program one by one and check for errors detected at the time while converting. With this, it is much easier to find errors than in a compiler. An interpreter is faster than a compiler because it executes the code immediately after reading it.
It is commonly used as a debugging tool for software development as it can execute a single line of code at a time. An interpreter is also more portable than a compiler because it is not always processor dependent, it can work across hardware architectures.
Assembler
An assembler is a translator used to translate assembly language into machine language. It’s like a compiler for the meeting language, but interactive like an interpreter. Assembly language is difficult to understand since it is a low-level programming language. An assembler interprets a low-level language, an assembly language, a lower-level just language, which is machine code. The device code can be understood immediately with the help of the CPU.
Advantages and disadvantages of translators
Here are some advantages of the compiler:
- All software is demonstrated so there are no machine errors.
- The executable report is superior in terms of the compiler, so it runs faster.
- Now it is not necessary to run this program on the same device on which it was created.
Here are some negative aspects of the compiler:
- Its execution is very gradual since all the software must be finalized.
- It is not easy to debug since errors are displayed at the end of execution.
- Hardware specific, it actually works on a specific machine language and architecture.
Here are some advantages of the interpreter:
- You discover the errors before completing this system, so you can investigate from your errors.
- The program can be run before completion so that you can get partial consequences without delay.
- You can work on small program components and link them later into a complete software.
Here are some negative aspects of the interpreter:
- There is a possibility of syntax errors in unverified scripts.
- The software is not more advantageous and may encounter information errors.
- could be slow due to translation on each run.
Here are some advantages of the assembler:
- Symbolic programming is easier to recognize and therefore saves the programmer’s time.
- It is much easier to fix errors and adjust the application instructions.
- execution performance like machine grade language.
Here are some assembler risks:
It is machine structured and cannot be used on different architectures.
A small alteration in the design can invalidate the entire request.
It is very difficult to sustain.
Presentation on theme: “The characteristics and purposes of Translators Translators, Interpreters and Compilers – High Level Languages.”— Presentation transcript:
1 The characteristics and purposes of Translators Translators, Interpreters and Compilers – High-level languages
2 mastery objectives Describe, with the resource For example, the features of languages of excessive degree. Explain the need for translators. Describe the distinction between interpretation and compilation.
3 gadget code computer system paintings and grasp the most useful gadget code. Simple instructions represented by a binary pattern on the laptop. Programming the system into code is time-consuming and subject to errors. Each preparation includes a code for the trade to be made and a binary illustration of the price to be manipulated/price trading to be manipulated, for example, 0100 0101, for example, 0100 0101, where 0100 means “jump” and 0101 is the trade to be made. . jump to.
4 high-level languages (HLL) similar to human languages and evolved for specific programs. FORTRAN (formula translation) evolved for technology and engineering applications and uses formulas in the same way that scientists and engineers do. FORTRAN (Formula TRANSLATION) was developed for technology and engineering applications and uses formulas in the same way that scientists and engineers do.
COBOL (Common Business Oriented Language) became advanced for enterprise applications. COBOL (Common Business Oriented Language) became advanced for business programs. It is much easier for humans to use it in HLL, but since computers only recognize device code, packages written in HLL must be translated into device code before they can be executed.
5 compiler Translates high-level languages into machine code. The device code model can be loaded on the device and run without any help as it is complete in itself. The high-level language version of the program is called source code, and the resulting device code application is called object code.
Note also that compilers produce “optimized” object code, this means “green” code; see Code Generation, Introducing Linkers and Loaders below. Also, note that compilers produce “optimized” object code, which means “efficient” code; see Code Generation, Introducing Linkers and Loaders below. Code generation, Presentation of linkers and loadersCode generation, Presentation of linkers and loaders
6 Risks of Compilers Use multiple active laptops. It must be loaded into the computer’s memory at the same time as the source code, and there must be sufficient memory to hold the product code. There should be enough memory to work in the garage while the performance is going on. The bugs within this proprietary software are difficult to pin down.
7 interpreters Take each training in turn and interpret it into the system code. Run translated coaching before subsequent coaching is translated.
8 Blessings of Interpreters: They need less memory than compilers (useful in early computers that had limited power and memory). They require less memory than compilers (useful in early computer systems that were power and memory restricted).
Continuously compiling all the code is a waste of time and is a waste of time during all testing, specifically if very small changes were made. Chronically compiling all code is wasteful and time-consuming during the verification process, particularly if very minor adjustments have been made.
During testing, the translator’s diagnostics will be more complete as error messages may occur related to the HLL being used and not the device code. At some point during the test, the translator’s diagnostics may be more complete, as error messages related to the HLL used and not the system code will be generated.
Since each error message is generated on the line where the error was found, it is much easier to identify/isolate the statement that is causing the problem. Since each error message occurs on the line where the error was found, it is much easier to find/isolate the formation that is causing the problem. Character segments can be executed without having to compile the entire software. People segments can be run without having to compile the entire program.
9 Dangers of Interpreters: Gradual execution compared to that of a compiled application because: Gradual execution compared to that of a compiled program because: The authentic application must be translated each time it is completed. Commands within a loop must be translated each time the loop is entered.
10 Interpreters and compilers Many high-grade languages use both. Programmers use the interpreter during program development, and while this system is fully operational, they use a compiler to translate it into device code. This version of device code can be assigned to users who no longer have access to the original code.
11 Plenary Why does software, written in a high-level language, want to be translated before it can run on a PC?
12 Complete computer systems only understand binary. HLL is written in a language close to human language. The translator needed to convert one into the opposite.
13 Plenary Describe the difference between interpretation and compilation.
14 Plenary Interpreter translates a line of code and then executes it. The compiler interprets the entire application before executing it. The compiler creates an item code. The interpreter preserves the source code. The compiler should be a knack for translation. The performer must be present for the performance.
Translators are multilingual professionals who can, of course, convert writings from one language to another. Their work is essential to make criminal, scientific and commercial texts available in different countries and languages. If you speak more than one language, meet the needs, and have the right skills, you could be a great translator. In this newsletter, we list the tasks, requirements and job types of the translator activity so that you can decide if this is the right career path for you.
What is the job of a translator?
A translator is hired to take texts written in one language and reproduce them in another. Your goal is to create a translation of the text that is accurate and reads the same as the original text. This involves maintaining the fashion, structure and tone of a report and decoding cultural references, expressions and jargon. Translators periodically read a text in a language they speak fluently and convert it into their native language. Translation process requirements may include:
- Read texts
- write and correct
- translate text from one language to another
- maintain the meaning, accuracy, and tone of the text
- perform a few rounds of revisions of the translated text
- improve computer-translated text
- discover technical or industrial terminology
- verify the quality and accuracy of a translation,
- creating subtitles for shows or movies,
- the use of online translation and computer-assisted translation equipment,
- consulting with company specialists,
- meeting with clients to determine their needs and ensure that the completed work meets their wishes,
- Provide clients with estimates of a Translation Challenge Cost and Timeline
- Stay up to date on translation tools and techniques
Translators typically work in the business, training, fitness, criminal, literary, scientific and technical industries. The texts they convert can consist of books, articles, published research, criminal documents and any other written material that needs translation.
Needs for translators
The maximum number of people who pursue a career as a translator speak at least two languages fluently. Clients and employers often look for translators with a bachelor’s degree, who enjoy the conversion of texts into different languages and the verbal exchange and interpersonal skills to reach this area. The translation activity requirements include:
Education
A translator’s education often begins in high school, where he or she attends and excels in foreign language training. Top translators earn their bachelor’s degree in a subject including translation, interpreting, global studies, English or a foreign language. Students who want to focus on translating certain styles of files can also study medicine, engineering, business, or law.
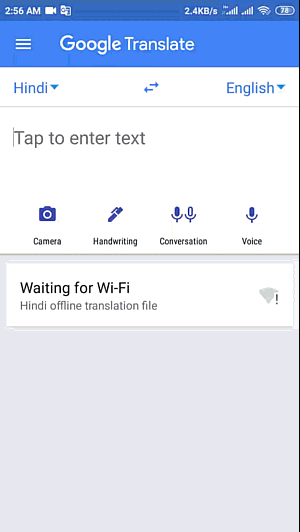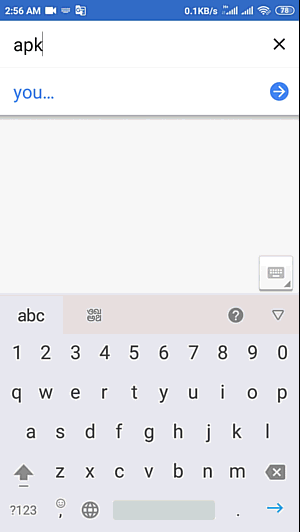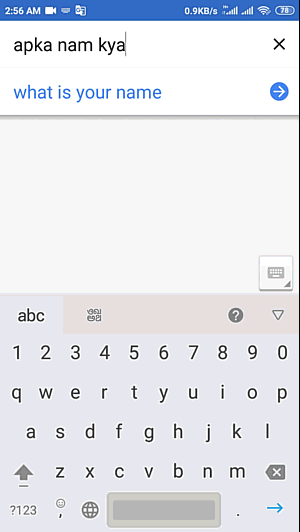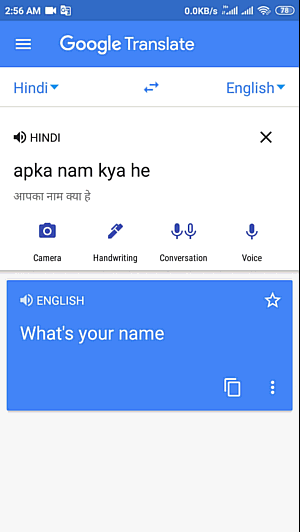
How to Translate English to Hindi
Language is a useful asset that interfaces individuals across the globe, empowering successful correspondence and the trading of thoughts. While English to hindi translation is one of the most broadly communicated in dialects worldwide, perceiving the significance of different dialects
https://24x7offshoring.com/translate-english-to-hindi/
While you can find translation jobs without a degree, especially if you speak some native languages, a bachelor’s degree can significantly improve your chances of landing a job and advancing in your profession. Most government and global companies, for example, require translators to have university levels.
The experience of enjoyment is one of the most important requirements to emerge as a translator, because you must exercise yourself by studying, writing and speaking a language to perfect it. To show employers that you can translate efficiently, gain experience through:
- Live abroad
- Interact and talk with people from other cultures
- Volunteer at hospitals, networking groups, and sporting events that attract athletes from around the world
- Get a paid or unpaid internship at a translation company
- Complete educational applications for positions that include a clinical or criminal translator community with other translators, and consider finding a mentor who can give you advice and help you find opportunities to gain experience. Expert agencies along with the American Translators Association (ATA) have tutoring applications.
Online Translation Jobs Translators can earn professional certifications to expose their talents and knowledge to competent employers. The ATA offers certification in 29 language combinations. Certification includes passing a 3-hour exam that requires you to translate portions of college-level content while following instructions for target audience, reason, and style.
Translators who skip this exam demonstrate their talent and ability to comply with the client’s instructions. To retain your license after passing the exam, you must earn 20 continuing education points every 3 years. You can also showcase your talents by passing assessments to translate content for companies like the US branch of Kingdom or the national virtual translation center. Skills The main skills that translators need to be successful and that they should have on their resume include: Attention to detail: Translators must pay close attention to the words, terms and expressions they translate to ensure that their work is accurate.
Business skills: Independent or freelance translators must have the business skills to connect with clients, market their offerings, and control their billing and finances.
Interpersonal talents: Translators work with a variety of clients and cultures and have to interact and speak with people correctly. The need to build strong and excellent relationships with customers if they want to get repeat business.
Many cutting-edge translators use computer-aided translation equipment to quickly convert text from one language to another. They may also use translation software and portable programs to publish the translated text to clients.
Time control: maximum translators work on deadlines and should be able to do their job correctly.
Writing and editing: Translators must have strong writing skills and display correct grammar, punctuation, and spelling in multiple languages.
Associate: Translator Skills: Definition and Examples
Translator Styles
Translators may focus on a positive type of job or industry, depending on their heritage. Types of translators include:
Financial: Banks, investment companies, and financial institutions may hire translators to convert financial reports, income statements, business plans, and other personal files into other languages.
Criminal: These translators work in courts or law offices to draft hearings, arraignments, trials, and other serious crime records in unique languages. They should understand complicated prison terminology.
Literary: Literary experts translate books, poems, articles, and short memoirs into unique languages. They can work carefully with authors and editors to maintain the style and tone of the content.
Scientific: These experts can work in health centers to help patients recognize scientific files. They can translate substances including clinical information, sanatorium website data, studies, information leaflets, pharmaceutical brochures and patient files from one language to another. Because medical translators regularly examine unique patient data, they must have excessive moral demands.
Medical: These translators work with complex content including medical journal entries, research summaries, and scientific texts. They generally have a historical background in an area such as chemistry or biology.
Associate: Eight Successful Translation Careers and Their Advantages
Prepare for Interviews with Exercise Questions and Tips Frequently Asked
Questions People interested in translation careers frequently ask the following questions:
How much money do translators earn?
Based on salaries, translators earn an average profit of $47,069 per year. Translators who work in specialized areas, are ATA licensed, or have many years of experience would likely earn higher salaries.
What is the painting environment of a translator?
Translators employed by companies or companies generally work full time in an office. Freelance translators work longer hours, are remote, and can work on numerous tasks at once. Employers of translators include:
Translation agencies, government companies , civil organizations such as police forces, healthcare facilities , laboratories or research organizations, courts, and criminal corporations with multiple clients
. Translators commonly work alone or in small companies. They can travel all over the world to exercise the languages they speak.
What professional development possibilities do translators have?
As translators become more skilled, they could:
- emerge as authorized translators
- take on additional tasks from employers
- receive more difficult tasks from clients
- start your own translation business
A successful freelance translator might even rent and manage a group of different translators and interpreters.
When you ask yourself what the function of a language translator is, it is possible to give you an answer as simple as this: The function of a translator is to convert textual content from the source language to the target language. You would be surprised to know that there is much more.
Here at 24x7offshoring, our community of translators can translate your files into over 200 languages across countless business categories and industries. And our specialists can translate these documents with methods that take into account language subtleties, cultural expectations, and other cultural nuances.
However, what exactly is a language translator and what does it do? In this article, we explore this very question.
Translation as a career
In his book Translation as a Profession, author Roger Chriss sums it up very well: “Translators are language specialists. They can be linguists, trained writers, diplomats and knowledgeable hobbyists. “
Like linguists, translators must be able to discern the subtleties and nuances of their languages, acquire knowledge of terminology and colloquialisms, and handle new trends in their languages.
Like writers, translators must be used to working long hours alone on a topic that interests few human beings and with a language that few around them understand.
Like diplomats, translators must be sensitive to the cultural and social variations that exist in their languages and be able to address those issues while translating. “
And as educated amateurs, translators need to recognize the basic concepts and some of the information about the topics they cover… The cardinal rule when you are not sure about a term or word is to ask.
An important part of the translator’s job is talking to the client, and a good translator knows when to invite questions.”
Case study: Learn how LinguaLinx helped translate 2.4 million words in 20 days
A translator is an author, the main function of a language translator is to write a piece of writing.
This may seem like a strange belief at first glance because the translator is not always the sole author of the text being translated, however, a good translation should read as if it were initially written in the destination.
A great deal of attention and knowledge goes into creating a translated text as easily as the original text, like writing a piece of writing from scratch.
Multitasking is essential.
Every other function of a language translator is to multitask like you have never imagined before. Here is a list of things a translator should do or not forget while working on a translation:
- capture the meaning of the source language
- Measure phrase choice for the target language
- conform to the source language format
- understanding or studying quality terminology for concern depends
- check for cultural differences in case it affects phraseology or grammar
- Convert proper names into a new one The alphabet, if relevant,
- ensures the overall readability and accuracy of the finished translation,
- which is quite important for an expert working on a text, not to mention that several of these things must be done simultaneously.
Translation is both a work of art and a science.
You cannot rely on a single device to successfully fulfill most of these responsibilities. It is unlikely that the same application can be trusted to systematize both grammatical and cultural nuances in one go.
Human translation is still a great need and should definitely be the option to translate your carefully worded material. Like many machines, humans make mistakes, but that’s why compliance is a crucial certification to look for and that any professional translation organization should have as part of their successful assurance technique demonstration.
Do you need expert translation offers?
If you need help translating your documents into almost any language and would really like to work with professional translators who understand both the source and target languages, click the link below to schedule a free consultation.
Translators work with written files to convey their meaning and style into different languages. They work predominantly with commercial, technical, criminal and clinical writings, although some translate fiction, poetry and screenplays. There are also specialized opportunities to work on video game text and film subtitles.
Translators differ from interpreters, who work with the spoken phrase.
Normal obligations consist of:
- Read and acquire knowledge of documents, terminology and linguistic styles,
- reproduce texts appropriately in single languages, often using professional software. Translation tends to be done from a “source language” (a language that is now
- not their local language) to their “target language” (their mother tongue),
- ensuring that the translated material is appropriate for the intended readers,
- consulting experts
- , increasing contacts and building relationships. with clients managing initiatives.
You may work modern “workplace” hours (nine to five), although you may no longer be able to be in an office. You may want to mark overdue or late times if a deadline is due or if a customer is in a specific time region.
Graduate Salaries According to Glassdoor, translator earnings tend to start at around £17,000 a year and can rise to around £29,000 with more experience. But, as it is common to be a self-employed translator, you may be paid according to your project, according to your word, or according to any other basis you have agreed with your clients.
As you develop your experience, your earnings will grow, as will your potential to focus on professional hobby areas. Glassdoor reports that translators in management positions earn around £48,000 per year.
Required qualifications and education.
Typically, you will need an undergraduate or graduate degree to become a translator. Expert graduate programs will introduce you to the approaches and software involved in professional translation, which could help your work programs stand out. Enjoyment of work can help here too – look into volunteer painting in case your degree doesn’t include a placement or you can’t find paid painting experience.
When you work, it is essential to continue learning about your selected languages and the cultures behind them. This can help you compete for works if you are a freelancer and could allow you to generate additional knowledge that you can bring to each project.
Key skills for translators
- The ability to work within time limits.
- The ability to quickly understand new ideas, for example technical terms.
- Cultural awareness and sensitivity.
- Clean writing with impeccable knowledge of spelling and grammar.
- Attention to the element.
- Mastery of at least foreign languages.
- The potential to build the best customer relationships.